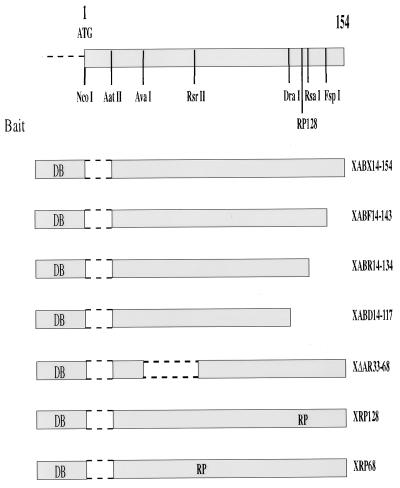
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram of the baits used in the study. To screen the HepG2 cell-derived cDNA library by the yeast two-hybrid screening, a stable bait was obtained by fusing the LexA DNA binding (DB) protein in frame with the HBx ORF deleted of its first 42 nt (XABX14-154) to create a 14-aa N-terminally truncated molecule. Several HBx mutants that include carboxy-terminal deletions (XABF14-143, XABR14-134, and XABD14-117) as well as an in-frame deletion (XΔAR33-68) and insertion of aa RP amino acid sequence (XRP128 and XRP68) were used to specifically identify and partially characterize, on a functional basis, the interacting XIP prey clone. A yeast vector carrying the amino acid substitution T36A in XIP failed to interact with the XABX14-154 bait, while a mutant with a T12A exchange did interact under the same experimental conditions.