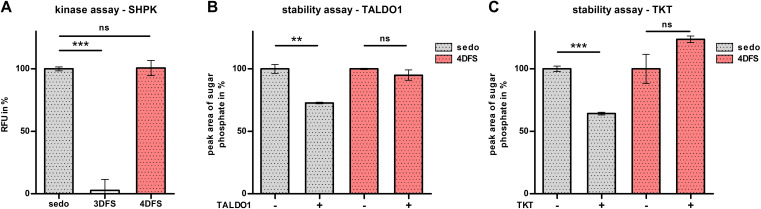
Figure 2.
A: Fluorescence‐based ADP‐accumulation assay with sedoheptulose kinase (SHPK). The graph represents the change in fluorescence signal arising from ATP consumption due to sugar phosphorylation by SHPK. Positive control (sedo) was normalized to 100 %. B & C: Enzymatic stability assays of 4DFS in the presence of SHPK and either transaldolase (TALDO1, B) or transketolase (TKT, C). The shown graph represents the peak area of the respective sugar phosphate after HILIC‐MS analysis compared to the negative (−) control samples (no TALDO1 or no TKT added) which were normalized to 100 %. Data is presented as the mean±standard error of mean (SEM) and was analyzed with an unpaired two‐samples t‐test: *** P<0.001, ** P<0.01, ns=not significant. RFU=relative fluorescence units, sedo=d‐sedoheptulose, 3DFS=3‐deoxy‐3‐fluoro‐d‐sedoheptulose, 4DFS=4‐deoxy‐4‐fluoro‐d‐sedoheptulose.