FIGURE A2.
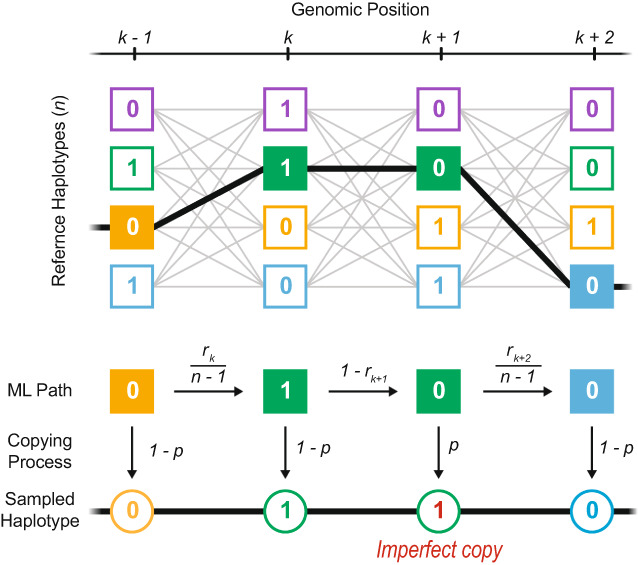
Schematic representation of Li and Stephens' (LS) hidden Markov model. A new haplotype can be sampled as an imperfect copy of n reference haplotypes (hidden states). To find the most likely path taken through the hidden states, the LS model works along the genome (k − 1, k, k + 1, …), calculating the probabilities of changes in the attributed haplotype. The transition probability to continue or switch the attributed haplotype is a function of the recombination rate (r) between adjacent sites, whilst the emission probability to copy the attributed allele with or without error is a function of the mutation rate (p). Moving along the genome, the LS model compares the probability of every possible copying path and infers the most likely one
