FIGURE 1.
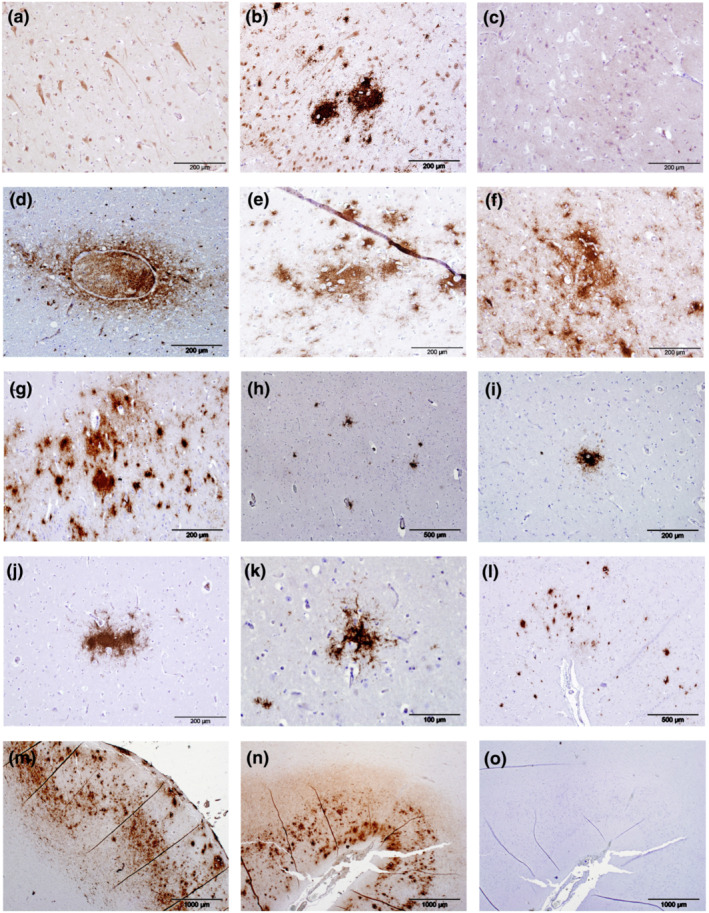
Immunolabelling (brown pigment) of amyloid‐beta peptide (Aβ) and amyloid plaques (APs) in the cerebrocortical grey matter of odontocetes. Aβ was present in the cell bodies of large neurons within the cerebrocortical grey matter and the labelling frequently extended into the axons (a, supralimbic/paralimbic/limbic lobes, animal Gg2). Intense labelling of Aβ was present in and around the nuclei in a small number of neurons with intensely labelled cytoplasm (b, limbic and anterior paralimbic lobes, animal Gm1). Some odontocetes had minimal intraneuronal labelling of Aβ represented by fine granular deposits within the cytoplasm (c, animal La1). Labelling of Aβ was present in and around a small number of the larger blood vessel (d, limbic and anterior paralimbic lobes, animal La5). When present, large deposits of Aβ in the neuropil in cerebrocortical layer I were diffuse, irregularly shaped with poorly defined borders with some coalescence forming APs present (e, supralimbic/paralimbic/limbic lobes, animal Tt1). When abundant, APs frequently coalesced (f, supralimbic/paralimbic/limbic lobes, animal Gm1; g, supralimbic/paralimbic/limbic lobes, animal Tt1). APs were distributed sparsely in animal La5 and did not coalesce (h, limbic and anterior paralimbic lobes). APs varied in shape and size within the same animal (i, limbic and anterior paralimbic lobes; j, supralimbic/paralimbic/limbic lobes; k, lingual lobe, all animal La5). Animal Gm1 had a medium number of APs present in the cerebrocortical grey matter, some of which had coalesced (l, supralimbic/paralimbic/limbic lobes). Animal Tt1 had the largest number of APs present, and these extended throughout all sections of cerebrocortical grey matter examined (m, supralimbic/paralimbic/limbic lobe). Positive control sections were composed of human brain tissue from a case of definitely diagnosed Alzheimer's disease (n). Sections used for negative controls were composed of semi‐serial sections of human brain tissue from a case of definitely diagnosed Alzheimer's disease (o) or positive odontocete brain tissue and were devoid of any immunolabelling
