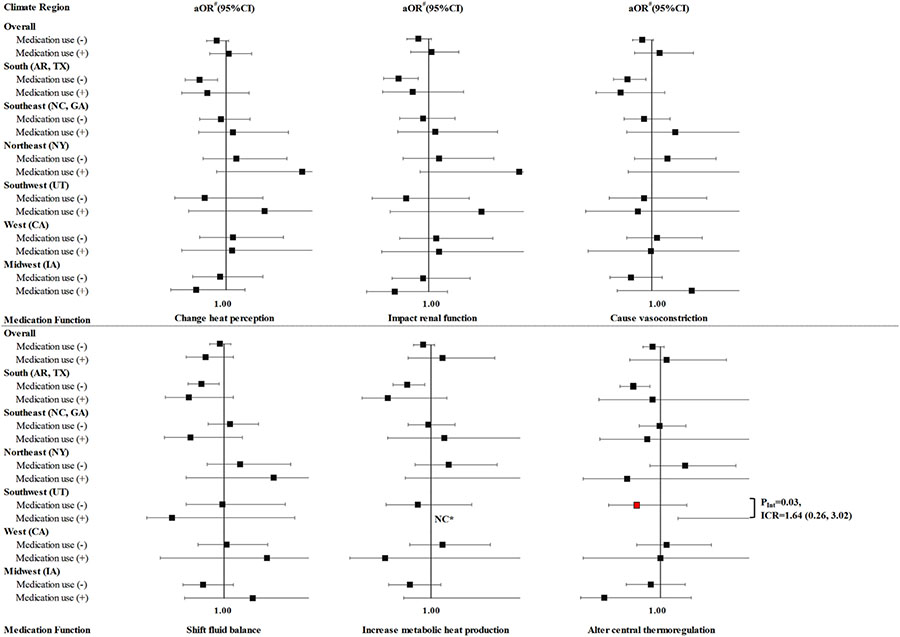
Fig. 1. Stratified aORs of the association between a summertime EHE90 in the residential area during the maternal critical period and CHDs among offspring, by maternal use of thermoregulation-related medication, by mechanism (Level 2) in eight states during the period from the month before pregnancy through the end of the 1st trimester, NBDPS, 1997–2007.
Exposure to medication was defined as self-reported use at least once during the month before conception through the end of the first trimester. # Referred to the participants unexposed to EHE90 and adjusted for maternal age (continuous), maternal race/ethnicity, and maternal education level. NC* indicated estimates for case groups with <3 exposed cases were not calculated. PInt indicated P value for EHE90*medication use. Abbreviationsa OR, adjusted odds ratio; AR, Arkansas; CA, California; CHD, congenital heart defects; CI, confidence interval; EHE, extreme heat event; EHE90, EHE was defined using the 90th percentile of daily maximum temperature for each study region during postconceptional weeks 3–8; GA, Georgia; IA, Iowa; ICR, interaction contrast ratio; NBDPS, National Birth Defects Prevention Study; NC, North Carolina; NY, New York; TX, Texas; UT, Utah.