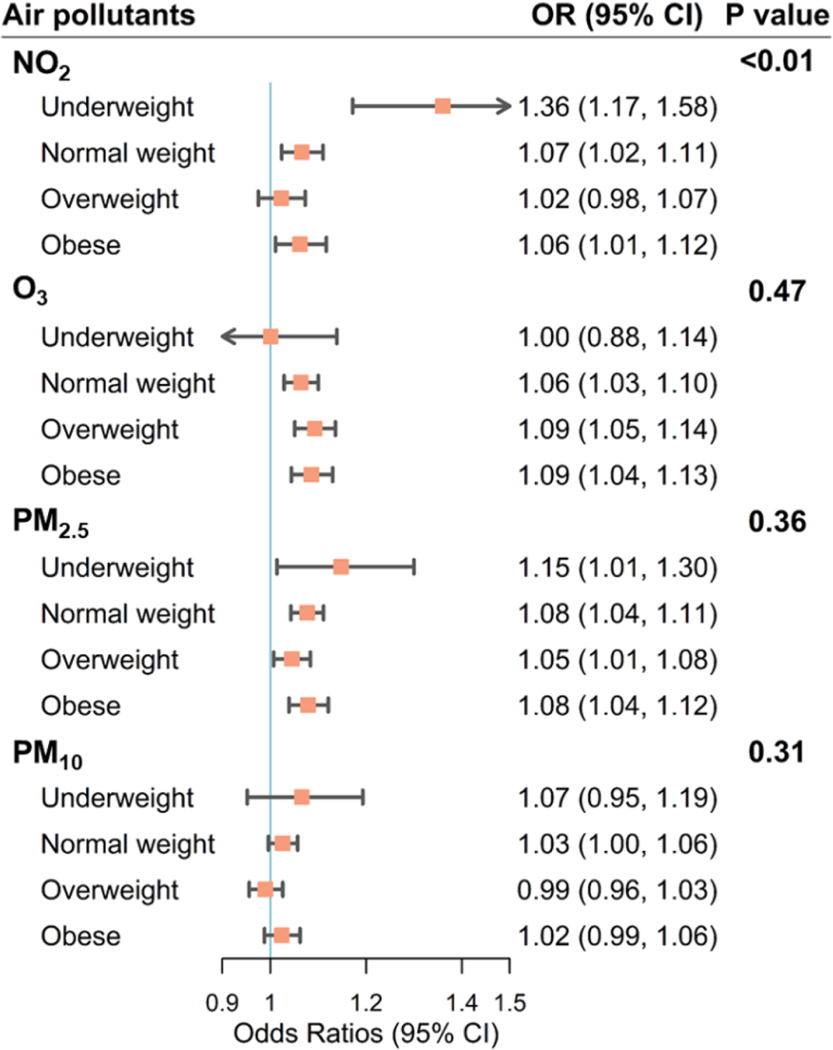
Fig. 2.
Subgroup analyses of associations (odds ratios [ORs] with 95% confidence intervals [CIs]) between air pollution exposure throughout the pregnancy and spontaneous premature rupture of membranes stratified by pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), kg/m2, where underweight refers to pre-pregnancy BMI < 18.5, normal weight refers to 18.5 ≤ pre-pregnancy BMI ≤ 24.9, overweight refers to 25.0 ≤ pre-pregnancy BMI ≤ 29.9, and obese refers to pre-pregnancy BMI ≥ 30.0. Exposure data were obtained from the empirical Bayesian kriging model. Models are adjusted for maternal age, race/ethnicity, education level, income level, smoking status, parity, year of infant birth, and season of conception. The p-value refers to the comparison among BMI subgroups and is obtained from Cochran’s Q test.