Fig. 2.
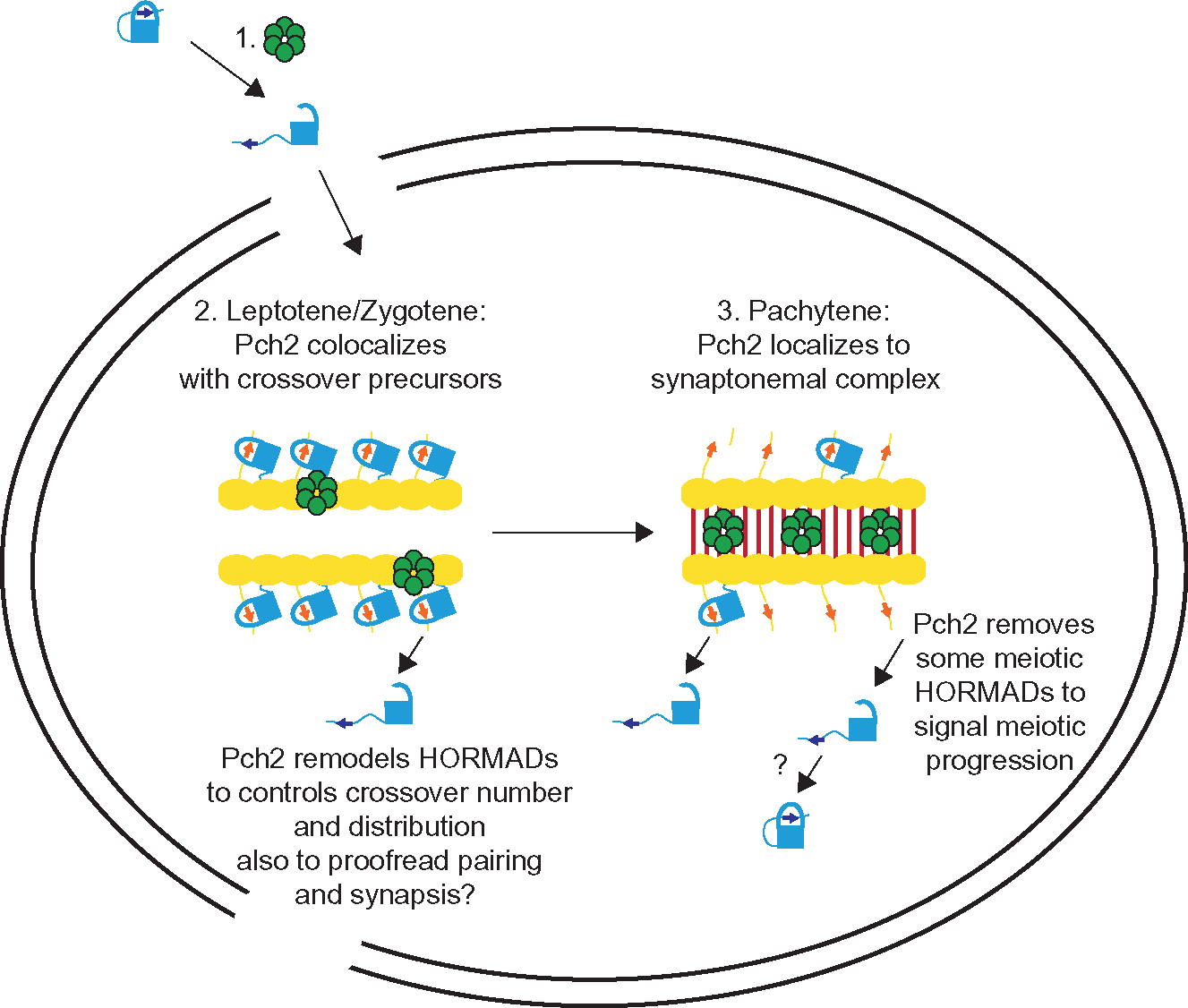
Model for Pch2/TRIP13/PCH2 function in systems in which recombination precedes synapsis, such as budding yeast, plants and mice. 1. Pch2 (green hexamer) remodels meiotic HORMADs from their closed conformation, bound to its own closure motif, to the extended conformation to enable its entry into meiotic nuclei and assembly on meiotic chromosomes. 2. During leptotene/zygotene, Pch2 forms puncta on meiotic chromosomes, colocalizing with crossover precursors, remodeling meiotic HORMADs from closed to extended to contribute to the gradual implementation of crossover number and distribution and possibly proofread homolog pairing and synapsis. Yellow ovals represent axis proteins that contain closure motifs and recruit meiotic HORMADs. 3. During pachytene, Pch2 localizes to the synaptonemal complex between synapsed homologous chromosomes, depleting meiotic HORMADs to limit meiotic recombination, drive meiotic progression and participate in the last stages of implementing crossover number and distribution through the remodeling of a reduced pool of meiotic HORMADs on meiotic chromosomes.
