Figure 3.
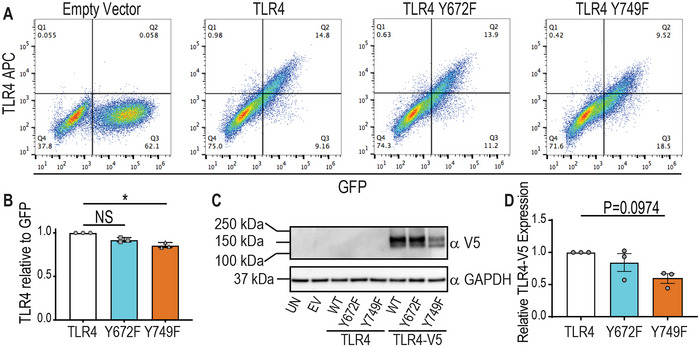
(A) TLR4 Y749F, but not a Y672F, mutation results in decreased levels of TLR4 protein. (A, B & D) Tlr4−/− BMM were reconstituted with WT mouse TLR4, the indicated TLR4 mutants or empty vector (EV). (C) Tlr4−/− BMM were reconstituted with V5‐tagged WT mouse TLR4, the indicated V5‐tagged TLR4 mutants or empty vector (EV). (A) Cells were assessed for transduction efficiency (plasmid coding for GFP) and surface TLR4 (APC anti‐TLR4 antibody) via flow cytometry. (B) The total number of APC (TLR4)‐positive cells was quantified as a ratio to the total number of GFP‐positive cells and plotted relative to the levels in BMM transduced with WT TLR4. (C) Whole cell lysates were collected and assessed for total TLR4 expression via western blot for α‐V5 (UN = untransduced control, EV = empty vector transduced control, WT = WT TLR4). (D) Western blots were quantified for total TLR4‐V5 expression (relative to GAPDH) and plotted relative to levels in BMM transduced with WT TLR4. (A & C) Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B & D) Data are combined from three independent experiments (mean ± SEM, n = 3) and statistical analyses were performed using a Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test (NS, non‐significant, *p < 0.05).
