Figure 7. ATRi and AKTi combination reduces tumor growth and prolongs survival, and high co-expression of DHX9 and AKT1 is associated with poor survival in HGSOC patients.
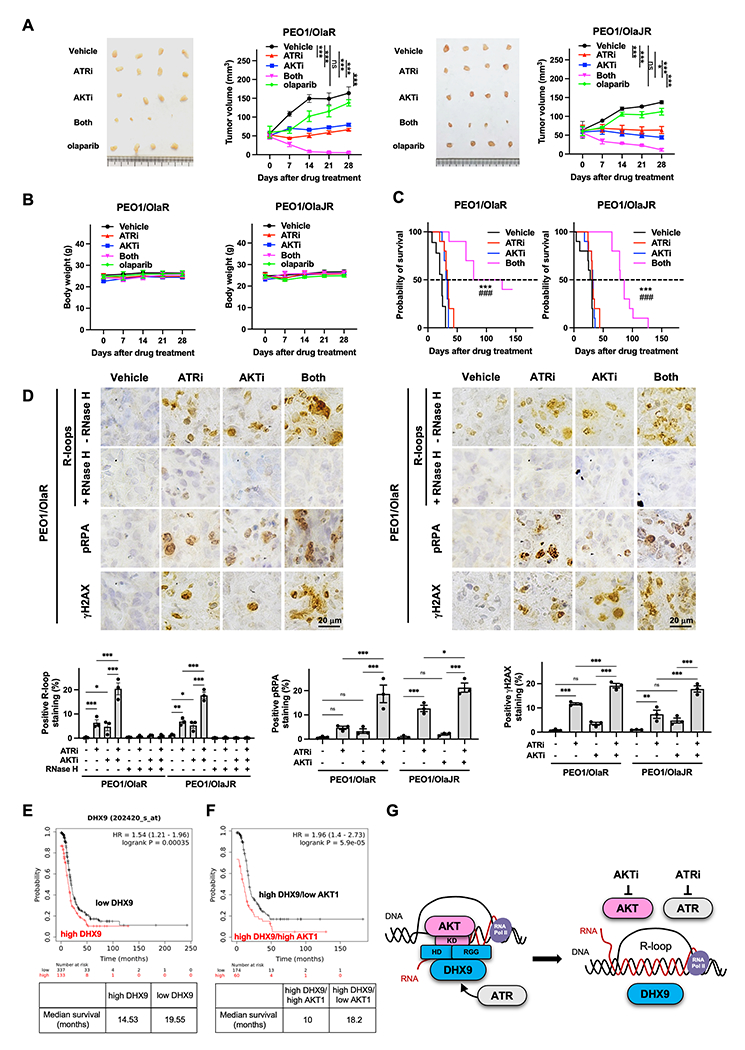
A-B, Tumor growth was measured using subcutaneous xenograft models (n = 4/group). Mice received vehicle, 130 mg/kg capivasertib, 50 mg/kg ceralasertib or 100 mg/kg olaparib. For combination, mice received 130 mg/kg capivasertib with or without 50 mg/kg ceralasertib. The tumor volume (A) and body weight (B) are plotted. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA test and shown as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant. C, Overall survival was studied using intraperitoneal injection models. Mice received vehicle, 130 mg/kg capivasertib and/or 50 mg/kg ceralasertib. Survival is shown by Kaplan–Meier curve using the Mantel-Cox log-rank test. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *, ATRi versus both; #, AKTi versus both; ***, ###, P < 0.001. D, Representative IHC images of R-loops, pRPA, and γH2AX (upper). The percentage of IHC positive staining area of nuclear R-loops, pRPA, and γH2AX are plotted (n = 3, bottom). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA test and shown as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant. E-F, Prognostic value of DHX9 and AKT1 was obtained from Kaplan–Meier plotter (http://kmplot.com/analysis/) [ovarian cancer] database. E, HGSOC tumors with high (n = 337) and low DHX9 levels (n = 133) were divided using auto-select best cutoff on the website. F, HGSOC with high DHX9 levels were further divided into high- versus low-expression groups based on the median expression of AKT1 using multiple genes analysis. The progression-free survival of patients with HGSOC was analyzed by Kaplan–Meier plotter website, and the hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals and log-rank P values were calculated. G, Proposed model of AKT1-dependent DHX9 function on R-loop resolution. While ATR is an important regulator of DNA replication and R-loop resolution, AKT1 also plays an essential role in R-loop resolution by directly recruiting DHX9 to R-loops through AKT1 kinase domain’s interaction with DHX9 helicase domain and RGG box. Hence, combined inhibition of AKT and ATR creates lethal replication stress by inducing aberrant R-loops in PARPi-resistant HGSOC.
