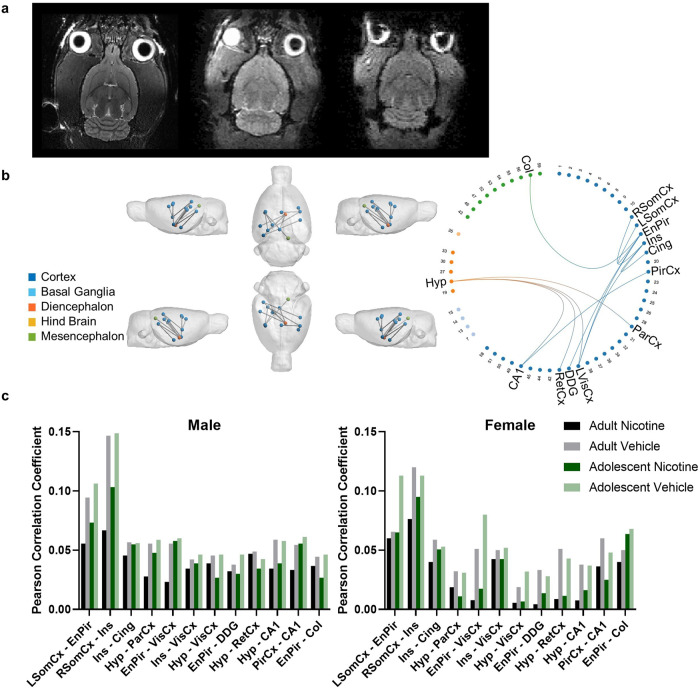
Fig. 5. Reduced functional connectivity was observed in nicotine vapour-exposed rats, with greater reductions observed in female rats.
a Representative single subject T2 anatomical image (left), diffusion b = 0 image (middle), and the first volume of an fMRI dataset (right). b NBS statistics confirmed reduced functional connectivity in the Nicotine group (n = 34) compared to the Vehicle group (n = 36) when controlling for age and sex (p = 0.013, 12 edges, 13 nodes). Significant edges have anatomical regions labelled. All other regions are labelled with their numerical SIGMA atlas reference. c Average Pearson Correlation Coefficients in edges identified by NBS statistics to have reduced functional connectivity in the Nicotine group when controlling for age and sex (p = 0.013, 12 edges, 13 nodes). Post-hoc analysis confirmed a statistically significant group by sex interaction effect (p < 0.001, 5 edges, 6 nodes). No statistically significant group-by-age interaction effect was confirmed. Abbreviations: L Left, R Right, Hyp Hypothalamus, ParCx Parietal Cortex, PirCx Piriform Cortex, EnPir Endo/piriform Cortex, VisCx Primary and Secondary Visual Cortex, CA1 Cornu Ammonis 1, SomCx Primary Somatosensory Cortex, Ins Insular Cortex, Cing Cingulate Cortex, DDG Dorsal Dentate Gyrus, RetCx Retrosplenial Cortex, Col Colliculus.