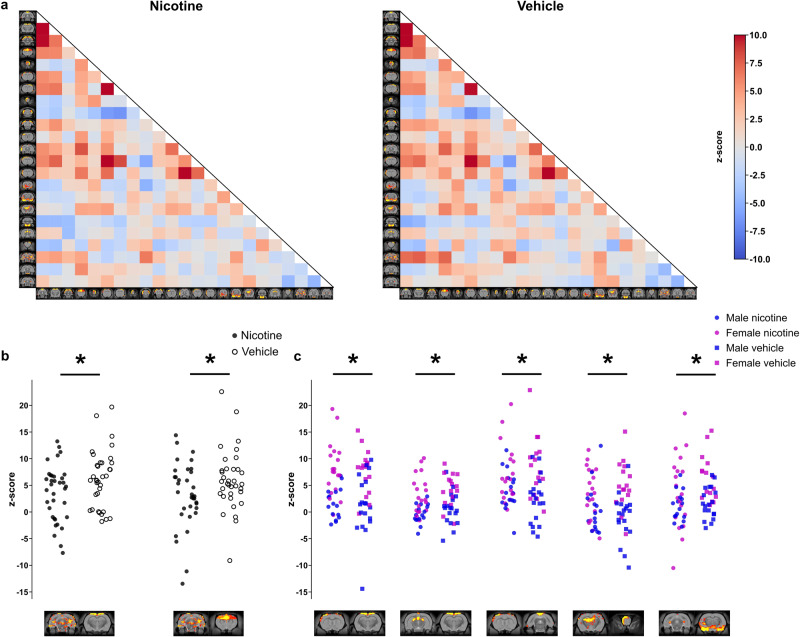
Fig. 6. Nicotine-exposed animals showed decreased between component group connectivity.
a Between-Resting state network average group connectivity. The values were calculated by averaging correlation coefficient within each group between the resting state networks resulting from the ICA. The results are shown as z-scores. b Significant differences in correlation strength were observed between nicotine and vehicle-exposed rats. Non-parametric permutation test was used (10,000 permutations). comparisons are adjusted for sex. A decrease in functional connectivity in animals exposed to nicotine vapour was seen between the hippocampus and the somatosensory cortex (left) components, and between the hippocampus and cingulate cortex (right) components. c Effects of sex on resting state network connectivity strength. Nodes showing significant interaction between sex and connectivity strength (ICA component pair-wise comparisons from left to right): Somatosensory and motor cortex, Hippocampus and somatomotor cortex, Somatosensory and default mode network, Hippocampus and olfactory bulb, Hippocampus and amygdala. FWER-corrected comparisons are presented. *p < 0.05.