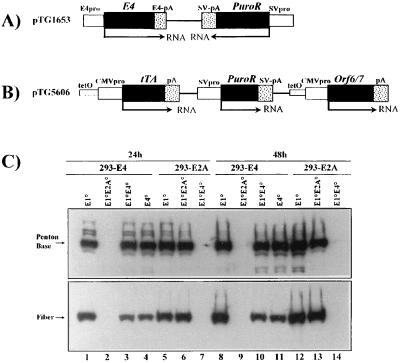
FIG. 3.
Structure of E4 expression plasmids and analysis of late viral proteins in 293-E2A and 293-E4 complementation cells. (A) Schematic representation of the E4 expression plasmid, pTG1653, containing the entire E4 region (Ad5 nt 32800 to 35826), including the E4 promoter (pro) and polyadenylation signal (pA). Expression of the puromycin resistance gene (PuroR) is regulated by the Simian virus 40 (SV) early promoter. (B) Schematic representation of the E4ORF6+7 expression plasmid, pTG5606. The tTA gene (26) as well as the E4ORF6+7 (Ad5 nt 32800 to 34219) genes are under the control of the minimal CMV immediate-early promoter fused to a heptameric tet operator (26), while the puromycin resistance gene is regulated by the simian virus 40 early promoter. (C) Analysis of late viral proteins in infected 293-E2A (clone 293/9-72; lanes 5 to 7 and 12 to 14) and 293-E4 (clone 293/5-19; lanes 1 to 4 and 8 to 11) complementation cells. Cells were infected with the indicated viruses at an MOI of 5 IU/cell (E1°, AdTG4656; E1°E4°, AdTG8595; E4°, AdTG9572) or 5 BU/cell (E1°E2°, AdTG9542). 293-E2A cells were induced with dexamethasone. All viruses contained the lacZ gene in place of the E1 region (Table 1), except for the vector AdTG9572, which contained an intact E1 region. Total protein extraction, electrophoresis, and Western blot analysis were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 1. Late viral proteins were detected with polyclonal antisera directed against the knob domain of fiber (serum E642; obtained from R. Gerard, Leuven, Belgium [31]) or against the penton base (serum SE262; obtained from P. Boulanger, Montpellier, France).