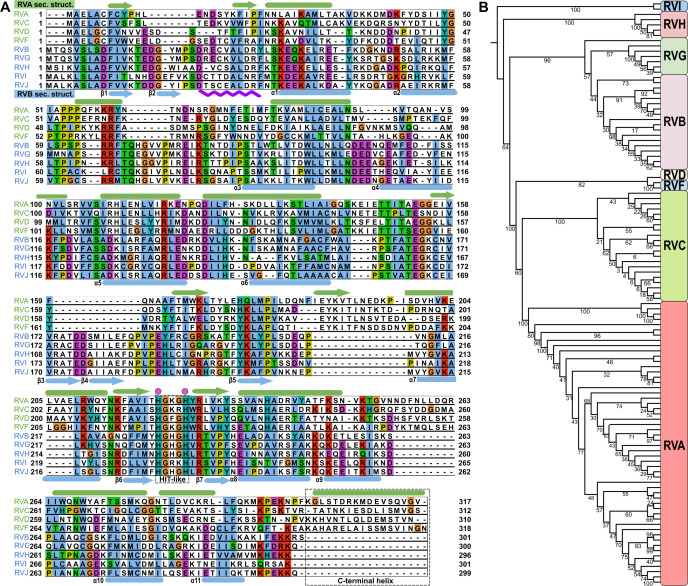
Fig 1.
Amino acid sequence comparison of different RV species. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of NSP2 from nine different RV species. Species that belong to the RVA clade (green) are at the top of the alignment. Species that belong to the RVB clade (blue) are at the bottom. Representations of RVA NSP2 secondary structures (green) are shown above the alignment panels. Representations of RVB NSP2 secondary structures (blue) are shown below the alignment panels. Arrows indicate β-strands. Cylinders indicate α-helices. The HIT-like motif and C-terminal helices are indicated by a gray rectangle. Conserved catalytic histidine residues are indicated by a pink dots above the alignment. The purple wavy line below the alignment represents a 10-amino-acid insertion in RVB NSP2. The following amino acid sequences were used: rotavirus A (PDB ID: 2R7C) (RVA), rotavirus B (AAF72868.1) (RVB), rotavirus C (AKH39851.1) (RVC), rotavirus D (AXL64569.1) (RVD), rotavirus F (AXL64586.1) (RVF), rotavirus G (AXF38053.1) (RVG), rotavirus H (QKY66970.1) (RVH), rotavirus I (AYH64828.1) (RVI), and rotavirus J (YP_010086027.1) (RVJ). (B) Phylogenetic analysis of NSP2 based on amino acid sequences from all nine RV species. Bootstrap values are indicated.