FIGURE 6.
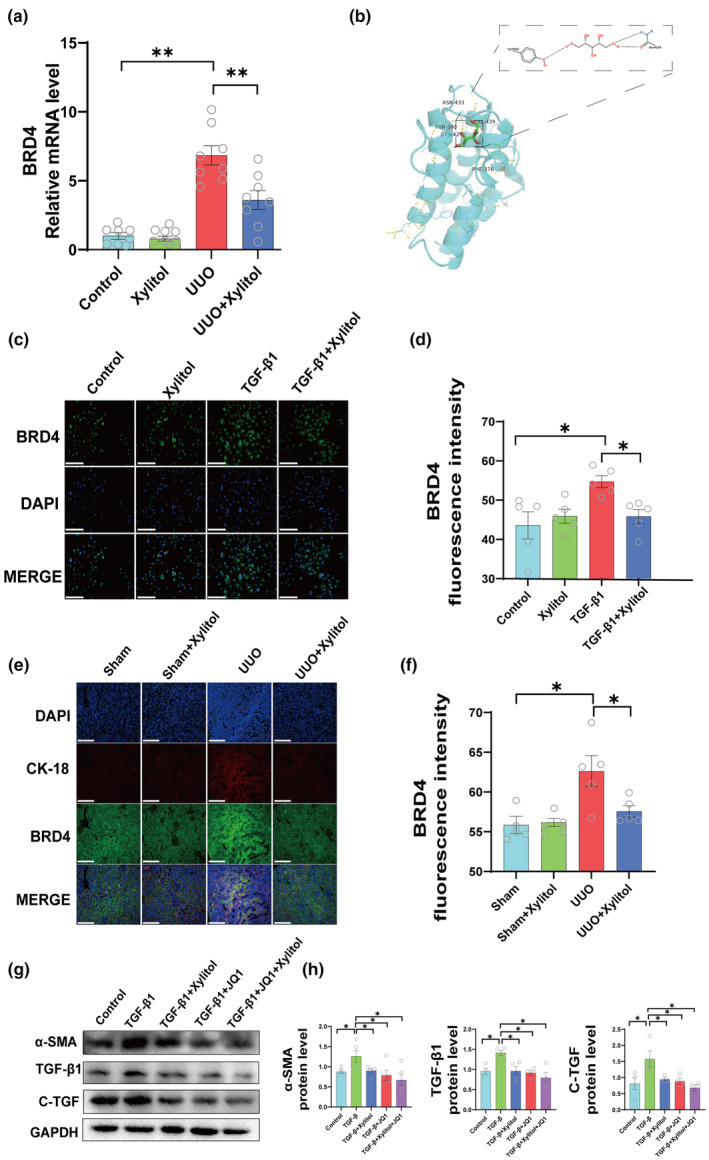
Xylitol attenuates renal fibrosis in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting BRD4 protein. (a) Left kidney qPCR experiments in mice of the sham group, sham + Xylitol group, UUO group, and UUO + Xylitol group. (n = 8). (b) Molecular docking to evaluate the interaction between xylitol and BRD4. (c, d) Immunofluorescence experiments against BRD4 in the control group, Xylitol group, TGF‐β1 group, TGF‐β1 + Xylitol group (IF, scale bar, 100 μm, magnification, ×400, n = 5). (e, f) Immunofluorescence experiments against BRD4 in the sham group, sham + Xylitol group, UUO group, and UUO + Xylitol group of mice left kidneys for BRD4 protein expression in tubular epithelial cells (IF, scale bar, 100 μm, magnification, ×400, n = 5). (g, h) Control group, TGF‐β1 group, TGF‐β1 + xylitol TGF‐β1 + JQ1, and TGF‐β1 + JQ1 + Xylitol groups for protein imprinting experiments of representative fibronectin by HK‐2 cells (n = 4). All of the in vitro experiments were conducted at least three times. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, and **p < 0.01. qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; UUO, unilateral ureteral obstruction.
