Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Geneformer pretrained and fine-tuned cell embeddings were robust to batch-dependent technical artifacts.
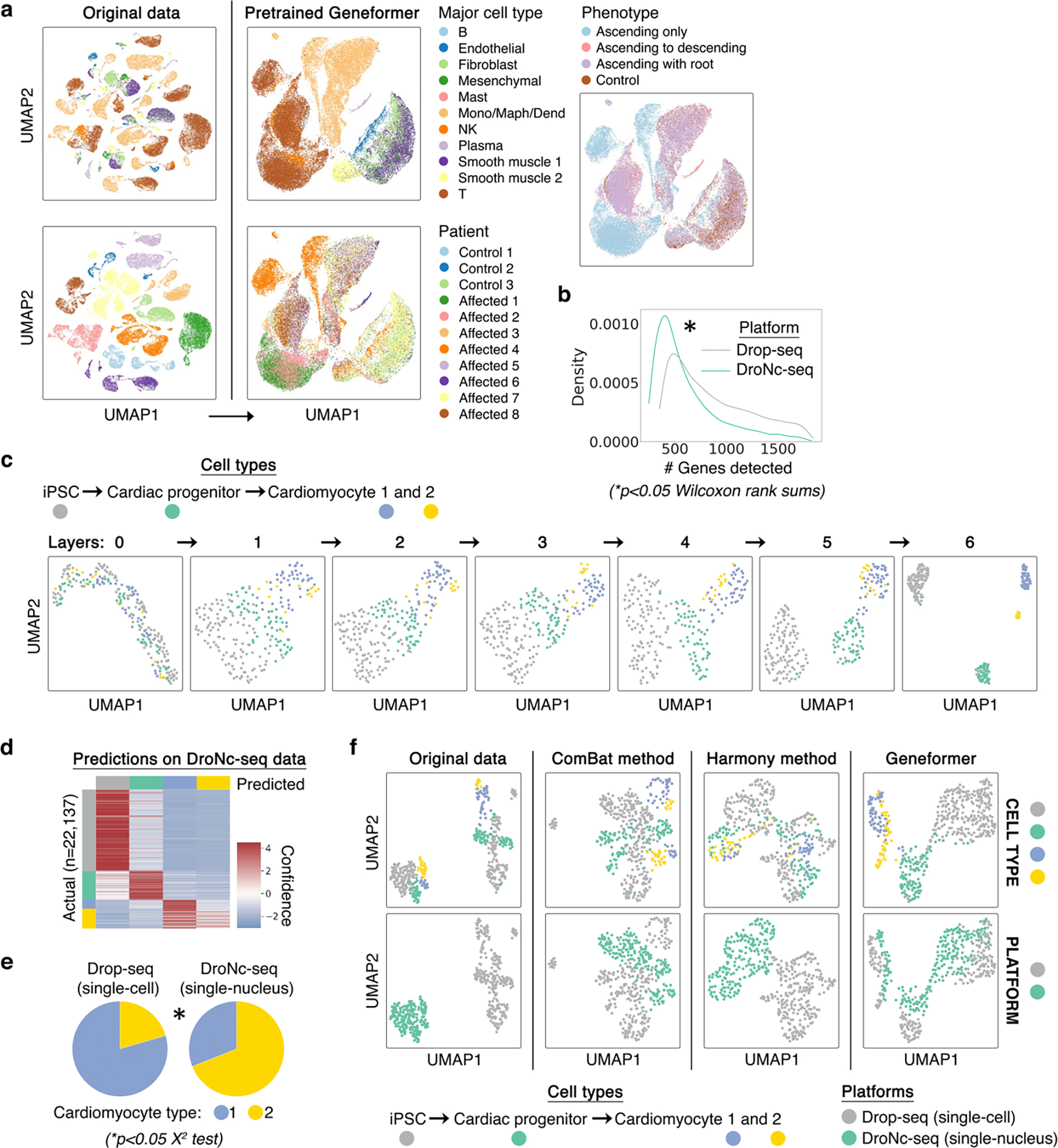
a, While original data (left) was highly affected by patient batch effect, cell embeddings generated by pretrained Geneformer (right) (without fine-tuning) clustered primarily by cell type and phenotype. Of note, affected individuals 1, 2, and 4 had the phenotype of ascending only aortic aneurysm, which is a different phenotype than aortic aneurysm that includes the root. b, Imbalance in the number of genes detected in each of the two platforms (single-cell Drop-seq versus single-nucleus DroNc-seq), which may result in batch-dependent technical artifacts. c, Cell embeddings from each layer of the Geneformer model fine-tuned to distinguish the indicated cell types (as annotated by original study11) using only the Drop-seq data. As the cells pass through each layer, the model successively extrudes them from each other to derive separable embeddings that distinguish the cell types. d, Cell type predictions on the DroNc-seq data by the model fine-tuned only on the Drop-seq data (out of sample accuracy 84%). Of note, inaccurate predictions were predominantly in predicting that cardiomyocyte type 2 was type 1, as expected given the minimal examples of cardiomyocyte type 2 in the Drop-seq data. e, The imbalance of cardiomyocyte type 1 and 2 between the platforms also suggests that these cellular subtypes may be an artifact of variable gene detection between the two platforms. f, Geneformer fine-tuned with only Drop-seq data automatically integrated DroNc-seq data such that the fine-tuned Geneformer cell embeddings primarily clustered by cell types and showed improved integration of platforms compared to the original data even after batch effect removal using the ComBat17 or Harmony18 methods.
