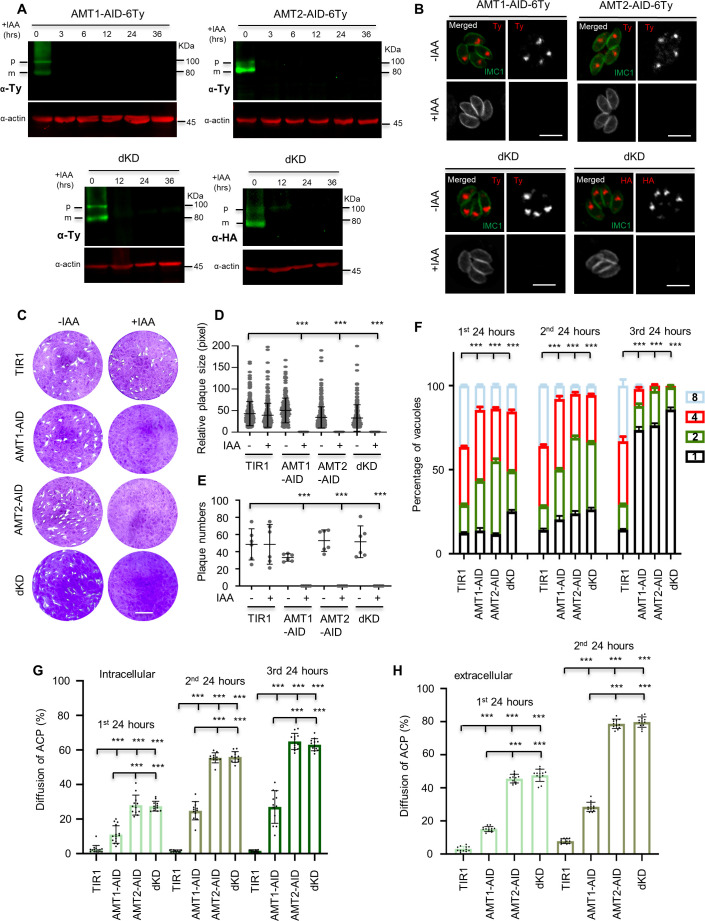
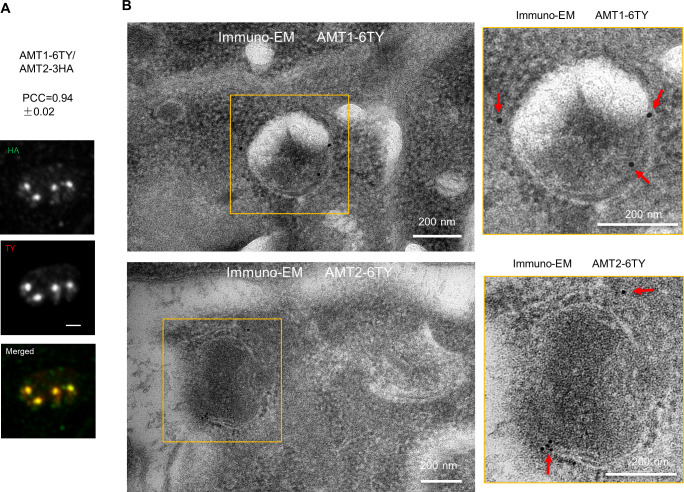
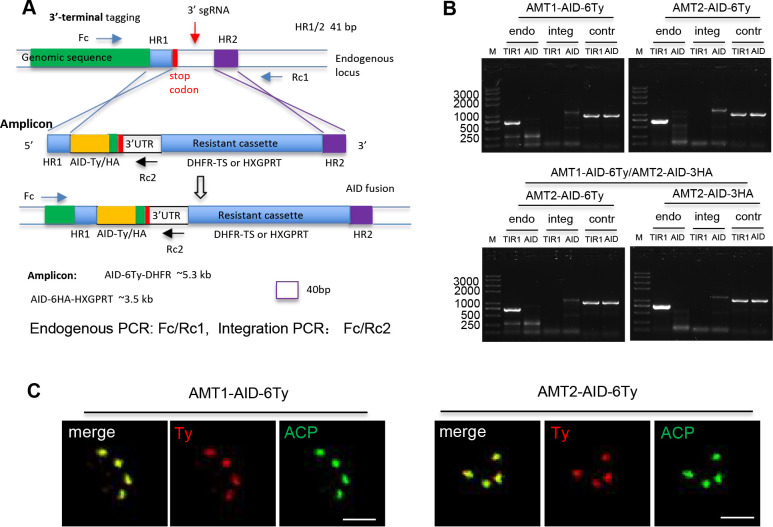
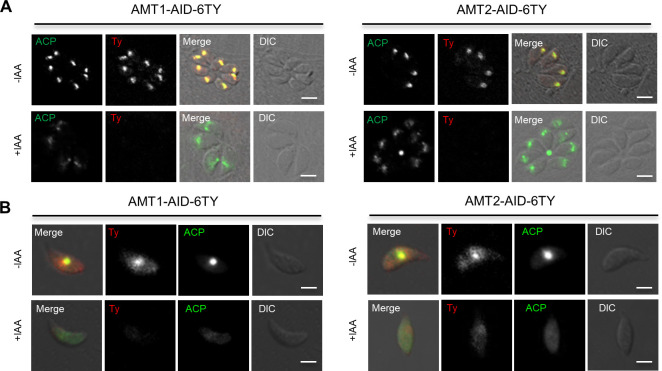
Figure 3. AMT1 and AMT2 are localized at the apicoplast membrane and essential for parasite growth in vitro.
(A) Western blot detection of protein depletion in the IAA-inducible degron (AID) lines. The lines were induced by auxin (IAA) for different hours (hrs) as indicated. Western blots detected immatured (p) and matured (m) forms of the protein fusions in the non-induced lanes. Actin served as the control. (B) Indirect fluorescence assay (IFA) detection of protein depletion in the AID lines. Parasites were grown in IAA for 24 hr, followed by IFA with antibodies against Ty or HA (red) and IMC1 (green). Scale = 5 μm. (C–E) Plaque formation by the TIR1 and AID lines on HFF monolayers in ±IAA for 7 days. Numbers (D) and sizes (E) of the plaques were measured by ImageJ. Scale = 0.5 cm. Two independent experiments with triplicates were performed. Data are shown as a mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). (F) Parasite replication of the TIR1 and AID lines grown in IAA. The parasites were grown in IAA for 24 hr, followed by scraping, harvesting and infection for the 2nd and 3rd rounds of parasite growth in IAA. The parasites stained with GFP45 were counted in vacuoles (at least 150 vacuoles in each replicate). In comparing to TIR1 (1st, 2nd, and 3rd), p < 0.0001 for the AID lines with 2 and 8 parasites/vacuole in the 1st round, and for the AID lines with 1–8 parasites/vacuole in the 2nd round, p < 0.0001 for the AID lines with 1 and 4 parasites/vacuoles in the 3rd round. (G, H) Acyl carrier protein (ACP) diffusion in the TIR1 and AID lines grown in IAA. Parasites were grown in IAA for the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd lytic cycles, as described in the parasite replication assay (intracellular parasites). Those parasites in the 1st and 2nd round of growth were forced to egress for the same analysis (extracellular parasites). Vacuoles or single parasites were scored (n > 150 for each replicate). Fields/images were selected blind and all parasites/vacuoles were scored on the same fields/images (F–H). Three independent experiments with triplicates were performed (A, B, C, F, G, and H), and representative images were shown for A, B, and C, data are shown as a mean ± SEM with two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparisons (compared with the TIR1). ***p < 0.0001.