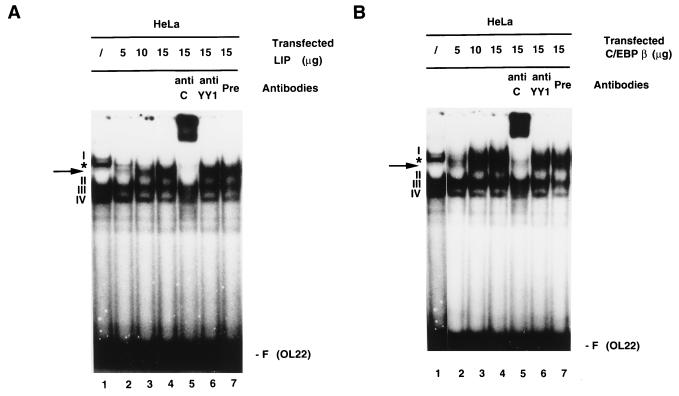
FIG. 3.
Overexpression of LIP or C/EBPβ in HeLa cells disrupts YY1-C/EBPβ complex formation on the switch region OL22. (A) Expression of LIP disrupts complex I and results in the formation of a new complex on OL22. HeLa cells were transfected with increasing amounts of CMV-LIP (5, 10, or 15 μg). 32P-labeled oligonucleotide OL22 was used in EMSAs, and anti-C/EBPβ antibodies, anti-YY1 antibodies, or preimmune serum was included in the binding reaction mixtures. Lanes: 1, standard binding reaction with extracts from nontransfected cells; 2 to 4, binding reactions with nuclear extracts from HeLa cells transfected with increasing amounts of CMV-LIP (lane 2, 5 μg; lane 3, 10 μg; lane 4, 15 μg); 5 to 7, binding reactions with nuclear extracts from cells transfected with 15 μg of CMV-LIP, incubated with anti-C/EBPβ antibodies (anti C), (lane 5), anti-YY1 antibodies (anti YY1) (lane 6), or preimmune serum (Pre) (lane 7). Specific DNA-protein complexes are indicated by numbers (I to IV). A nonspecific DNA-protein complex is indicated by an asterisk. The new complex formed on OL22 through expression of transfected CMV-LIP is indicated by an arrow. F (OL22), free probe OL22. (B) Expression of C/EBPβ leads to the formation of new complexes on OL22. Essentially the same experiments as described for panel A were carried out, but a plasmid expressing C/EBPβ was used instead of a LIP-expressing plasmid. The EMSA products shown in panels A and B were resolved on a 6.5% polyacrylamide gel.