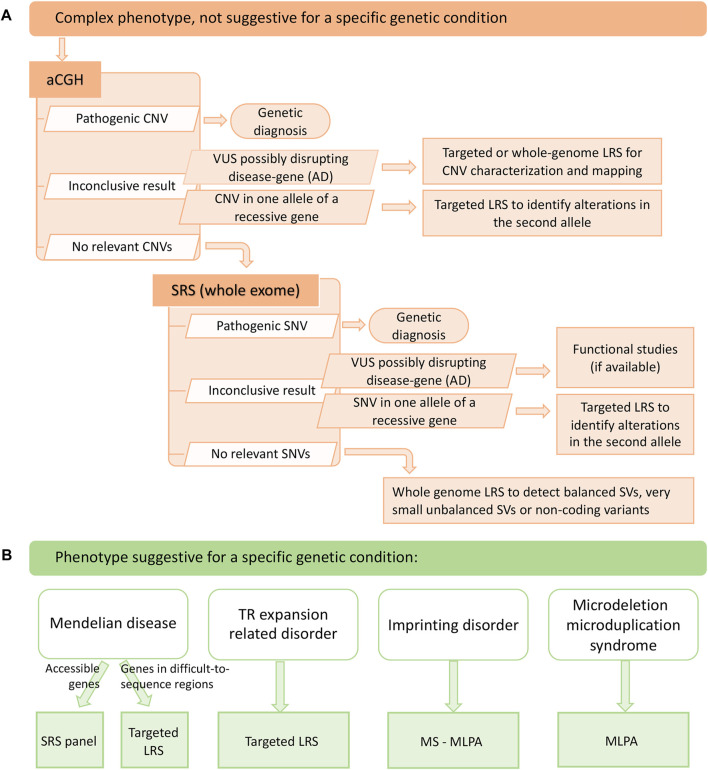
FIGURE 2.
Suggested diagnostic workflows that include long read sequencing. (A) diagnostic workflow to be adopted in case the patient presents with a complex phenotype, not suggestive for a specific genetic condition. Long read sequencing can help define copy number variants of uncertain significance, a targeted approach can be useful to study the second allele of a recessive gene when a monoallelic variant is identified and, finally, a whole genome approach can be an additional diagnostic tool in case neither single nucleotide variants nor copy number variants are detected with other techniques. (B) diagnostic workflow to be adopted in case the patient presents with clinical features that are suggestive for a specific genetic condition. Targeted long read sequencing can help diagnose mendelian diseases involving difficult-to-sequence genes and tandem repeat-related disorders. aCGH: array-comparative genomic hybridization; AD: autosomal dominant; CNV: copy number variant; LRS: long read sequencing; MLPA: multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification; MS-MLPA: methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification; SRS: short read sequencing; SNV: single nucleotide variant; SV: structural variant; TR: tandem repeat.