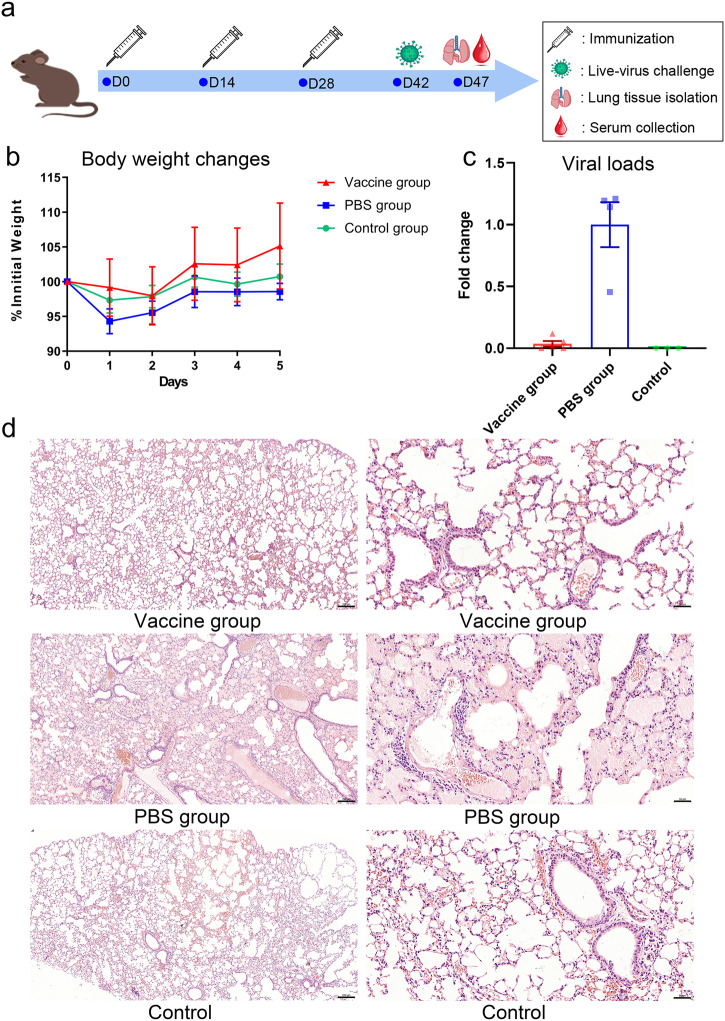
Fig. 5. The designed RBHcAg_MIR-II_NC-VIII provided high protective efficacy in mice against challenge with live RSV A2 strain.
BALB/c mice (n = 8 per group) were immunized intraperitoneally with RBHcAg_MIR-II_NC-VIII plus MF59-like adjuvant (vaccine group) or with PBS (PBS group) on days 0, 14, and 28, which were then challenged by RSV A2 strain on day 14 after the final immunization. Another group of mice (n = 4) was immunized and challenged with PBS as a control. Upon virus challenge, mouse body weights were measured. On day 5 after virus challenge, mice were sacrificed and their lung tissues were isolated, and then the virial loads in the lung tissues were detected and the histopathological changes were observed. a Timeline of mouse immunization, live-virus challenge, and lung tissue harvesting. b The body weight changes of the mice from different groups after virus challenge. One day after virus challenge, a mouse in the PBS group died and was removed from the analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. c Comparison of the viral loads in the lung tissues of the mice from different groups. The viral load was tested using the reverse transcription real-time PCR, which was then analyzed by the comparative cycle threshold (Ct) method using the GAPDH gene as the calibrator. Detection results were reported as the fold changes of the viral loads in comparison to the mean value of the PBS group. Five, four, and three mice in the vaccine, PBS, and control groups, respectively, were used for viral load detections. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. d Histopathological images of the lung tissues from different groups of mice challenged with RSV A2 live virus. The remaining three, three, and one mouse in the vaccine, PBS, and control groups, respectively, were used for the histopathological examinations. Lef images: magnification 5× and scale bar 200 μm; Right images: magnification ×20 and scale bar 50 μm.