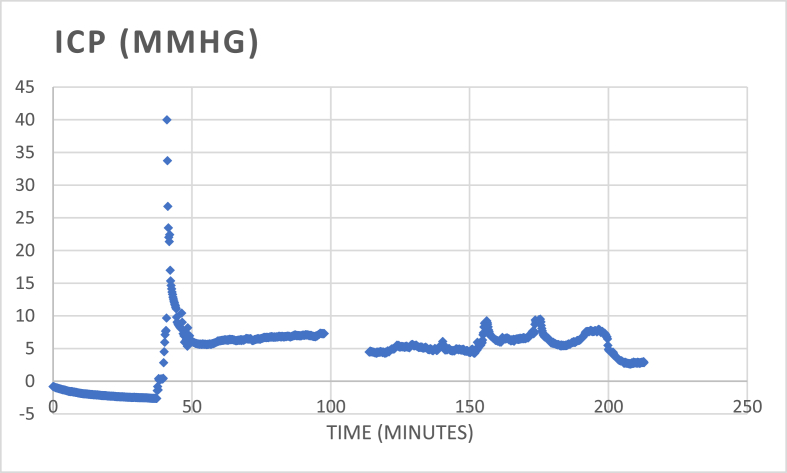
Fig. 4.
Overview of the time-curve of ICP of the Neurovent-probe in one animal (experiment 3). At time zero, the catheter is zeroed while holding still in water. The catheter is then removed from the water and exposed to the air, which shows a small drift of the value to −2.5 mmHg. Meanwhile, the skin is opened, and the skull is exposed. The impulse is then performed while the skull is intact. Directly after the impulse, the three boreholes are made. The LDF probe is placed in the medial borehole on intact dura, the dura of the two other boreholes is opened to place the Neurovent- and Codman-catheters in the parenchyma. The measurement catheters are in place within 10 min after the impulse, at that time the rapid decrease of high levels of ICP is seen. The highest measured ICP in this experiment measured 40 mmHg. For the remaining time of monitoring, ICP remained stable between 5 and 10 mmHg.