Figure 2. NPY-expressing sympathetic axons primarily innervate blood vessels.
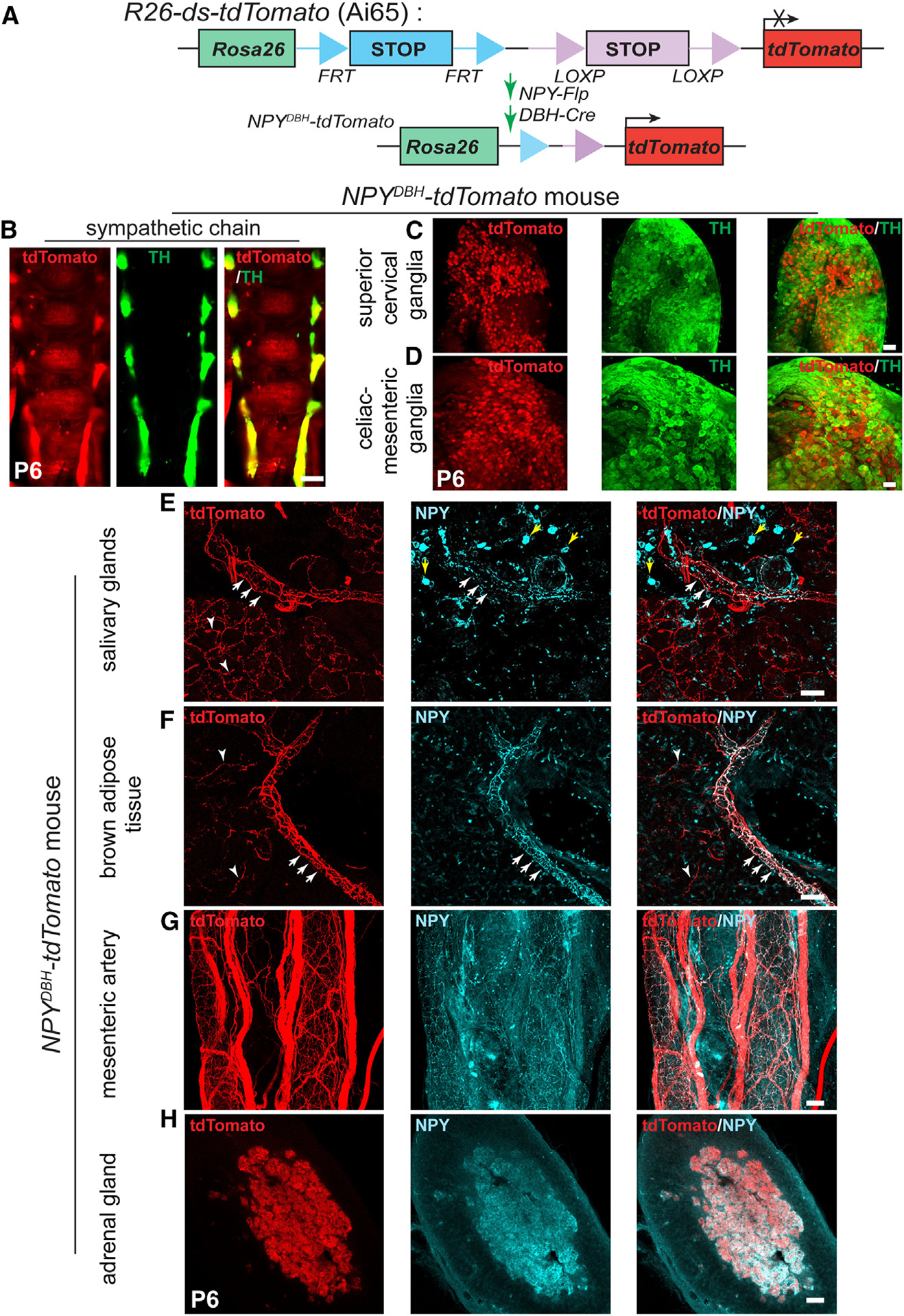
(A) Schematic showing the intersectional genetic strategy to generate NPYDBH-tdTomato mice, where tdTomato expression is activated by removal of two STOP cassettes by Flpo and Cre recombinases in sympathetic neurons co-expressing NPY and DBH.
(B–D) Co-localization of tdTomato and TH in sympathetic chain (B), SCGs (C), or CG-SMGs (D) using whole-mount immunostaining in NPYDBH-tdTomato mice at P6. Scale bars, 500 μm (B) and 100 μm (C and D).
(E and F) Innervation of paravertebral targets (salivary glands, BAT) by NPYDBH-tdTomato sympathetic fibers. tdTomato signal (red) is observed in axons aligned with blood vessels (white arrows) as well as in tissue parenchyma (white arrowheads). Compared to reporter expression, axonal NPY immunostaining (cyan) is only found in axons associated with vasculature. Yellow arrows indicate NPY immunostaining in non-neuronal cells. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(G and H) Co-localization of NPY protein and tdTomato reporter expression in mesenteric artery (prevertebral sympathetic target, G) and adrenal chromaffin cells (H). Scale bar, 50 μm.
