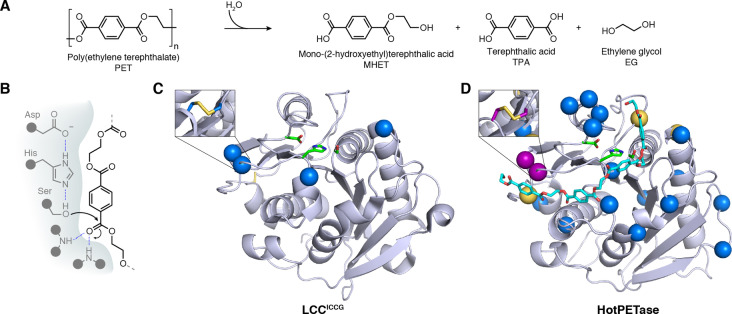
Figure 5.
PET depolymerisation. A) Various enzymes capable of hydrolysing PET to MHET, TPA and EG have been discovered to date. B) PET deconstructing enzymes typically belong to the cutinase enzyme family, which are serine hydrolases and utilize a catalytic triad in conjunction with an oxy‐anion hole. C) LCCICCG is an engineered PETase derived from leaf‐branch compost cutinase. [69] Four mutations (blue spheres) were introduced to increase thermostability (i.e. through installation of a disulphide bridge) (PDB: 7 W44 [75] ). D) HotPETase (model with docked PET substrate (cyan) based on PDB: 7QVH) was engineered for increased thermostability from the natural enzyme IsPETase through rational design (yellow & purple spheres) and directed evolution (blue spheres). A total of 24 mutations were introduced leading to a T m increase of 34.5 °C. [75] (Diagram abbreviations: PET=poly(ethylene terephthalate), MHET=mono‐(2‐hydroxyethyl) terephthalic acid, TPA=terephthalic acid, EG=ethylene glycol, LCC=Leaf‐branch compost cutinase).