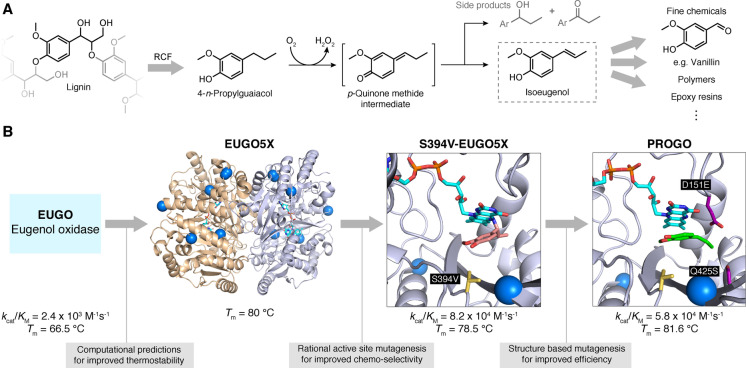
Figure 6.
Lignin as a chemical feedstock. A) Lignin can be depolymerised by RCF, yielding 4‐n‐propylguaiacol as a main product. VAO‐type oxidases convert 4‐n‐propylguaiacol to isoeugenol as well as 4‐(1‐hydroxypropyl)‐2‐methoxyphenol and 1‐(4‐hydroxy‐3‐methoxyphenyl)‐1‐propanone which emerge as side products via hydration of the methide intermediate. Isoeugenol is a versatile precursor for various fine chemicals and polymers. B) Eugenol oxidase (EUGO) was converted into an efficient catalyst for isoeugenol production, by introducing mutations that improve thermostability (blue spheres), chemo‐selectivity (S394 V‐EUGO5X: yellow sticks) and to protect the FAD cofactor (cyan sticks) by preventing adduct formation with the substrate (PROGO ‐ D151E & Q425S: purple sticks). [95] The crystal structure of S394 V‐EUGO5X (PDB: 7YWU) shows the formation of a covalent adduct between the substrate (salmon) and FAD, which is absent in the PROGO crystal structure (PDB: 7YWV, substrate shown in green). (Diagram abbreviations: FAD= flavin adenine dinucleotide, RCF=reductive catalytic fractionation).