FIGURE 4.
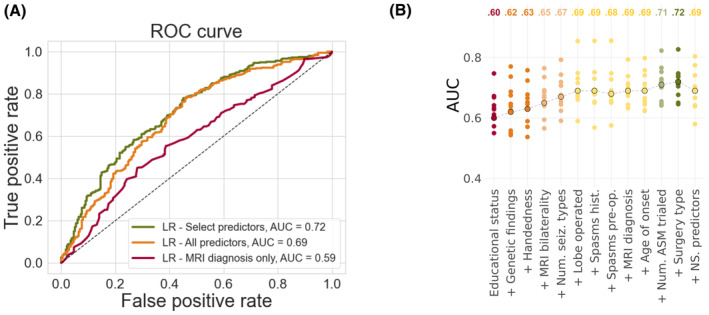
Impact of feature selection on model performance. (A) Receiver‐operating characteristic (ROC) curves showing model performance for our LR models containing (1) only MRI diagnosis (red), (2) all predictors (orange), and (3) predictors identified through data‐driven feature selection (green). Data‐driven selection involved including only predictors that were significantly predictive of 1‐year postoperative seizure outcome as identified in univariable logistic regression analyses. Corresponding ROC curves showing model performances for our MLP and XGBoost models are displayed in Figures S2 and S3. (B) Effect of data‐driven feature selection on model performance (AUC). Variables found to be significantly predictive of seizure outcome from univariable logistic regression analyses were added to the LR, from most information to least informative according to their coefficients. Model performance was best when all significantly predictive features were included in the model. Adding the remaining predictors collected for the study, that is, those that were not significantly predictive of seizure outcome, worsened model performance (far right). Points circled in black represent mean AUC obtained across all 10 folds. Noncircled points represent the AUCs obtained from each of the individual 10 folds. ASM, antiseizure medication; AUC, area under the (ROC) curve; LR, logistic regression; NS. predictors, non‐significant predictors; Num. ASM trialed, total number of different antiseizure medication trialed from epilepsy onset to preoperative evaluation; Num. seiz. types, number of seizure types at time of preoperative evaluation; ROC, receiver‐operating characteristic; Spasms hist., history of spasms; Spasms pre‐op, spasms at time of preoperative evaluation.
