Fig 5.
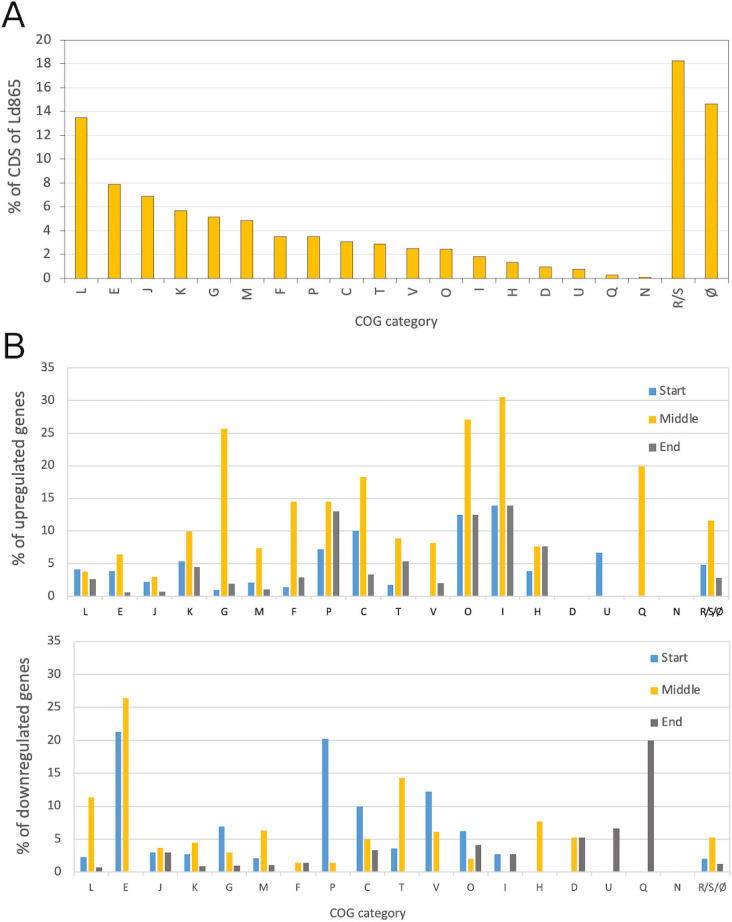
COG classification of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii CIRM-BIA865 coding sequences (A) and transcription level during soy juice fermentation (B). (A) COG database categories of coding sequences (CDS) in Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii CIRM-BIA865 (Ld865) whole genome. Data are expressed as percent of total CDSs of the genome. The genome of Ld865 contains 1962 CDS, and 84.5% of the CDSs can be classified in a COG category. (B) For each COG category, percentage of genes differentially expressed (DE), between three successive steps of fermentation of soy juice by Ld865. Up: genes upregulated; down: genes downregulated. Blue bars: between pHs 6.5 and 6.0 (start of fermentation); Orange bars: between pHs 6.0 and 5.0 (middle of fermentation); Blue bars: between pHs 5.0 and 4.6 (end of fermentation). 100% represent all the genes classified in the COG. For example, between pHs 6.5 and 6.0 (start of fermentation), 3.9% and 21.3% of all the CDSs belonging to COG E are up and downregulated regulated, respectively. (A and B) The letter codes for COG (Clusters of Orthologous Genes) database categories are C, energy production and conversion; D, cell division and chromosome partitioning; E, amino acid transport and metabolism; F, nucleotide transport and metabolism; G, carbohydrate transport and metabolism; H, coenzyme metabolism; I, lipid metabolism; J, translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis; K, transcription; L, DNA replication, recombination, and repair; M, cell envelope biogenesis, outer membrane; N, cell motility and secretion; O, post-translational modification, protein turnover, and chaperones; P, inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, secondary metabolite biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism; T, signal transduction mechanisms; U, intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; V, defense mechanisms; S, function unknown; R, general function prediction only; and Ø, no category attributed.
