Figure 2. Causes of motion artifact.
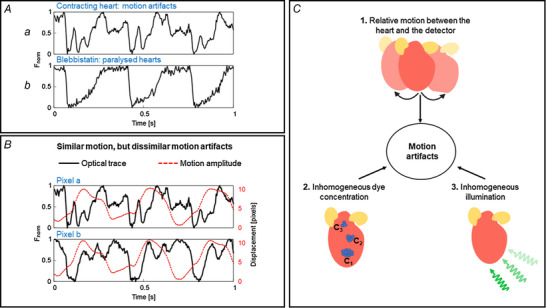
A, example traces of optical action potentials (OAPs) from a Langendorff‐perfused rabbit heart with and without contractile motion. Optical action potentials in contracting condition are characterized by motion artifacts as indicated by the distortions in the baseline and the repolarization phase of action potentials, whereas OAPs are not distorted when the motion is suppressed using blebbistatin. B, variation of motion artifacts and motion amplitude at two different locations (pixel a and pixel b, ∆d pixel = 7 mm) on the heart. OAPs (continuous black line) from the pixels are distorted differently and hence the motion artifacts are different at these locations despite similar contractile motion amplitudes (dashed red line), indicative of other factors, including inhomogeneous illumination and dye loading, which can contribute to the motion artifacts. C, factors contributing to motion artifact: relative motion between the heart and the detector, inhomogeneous illumination, and variations in dye concentration. A and B are modified from our previous study (Kappadan, 2021).
