FIGURE 4.
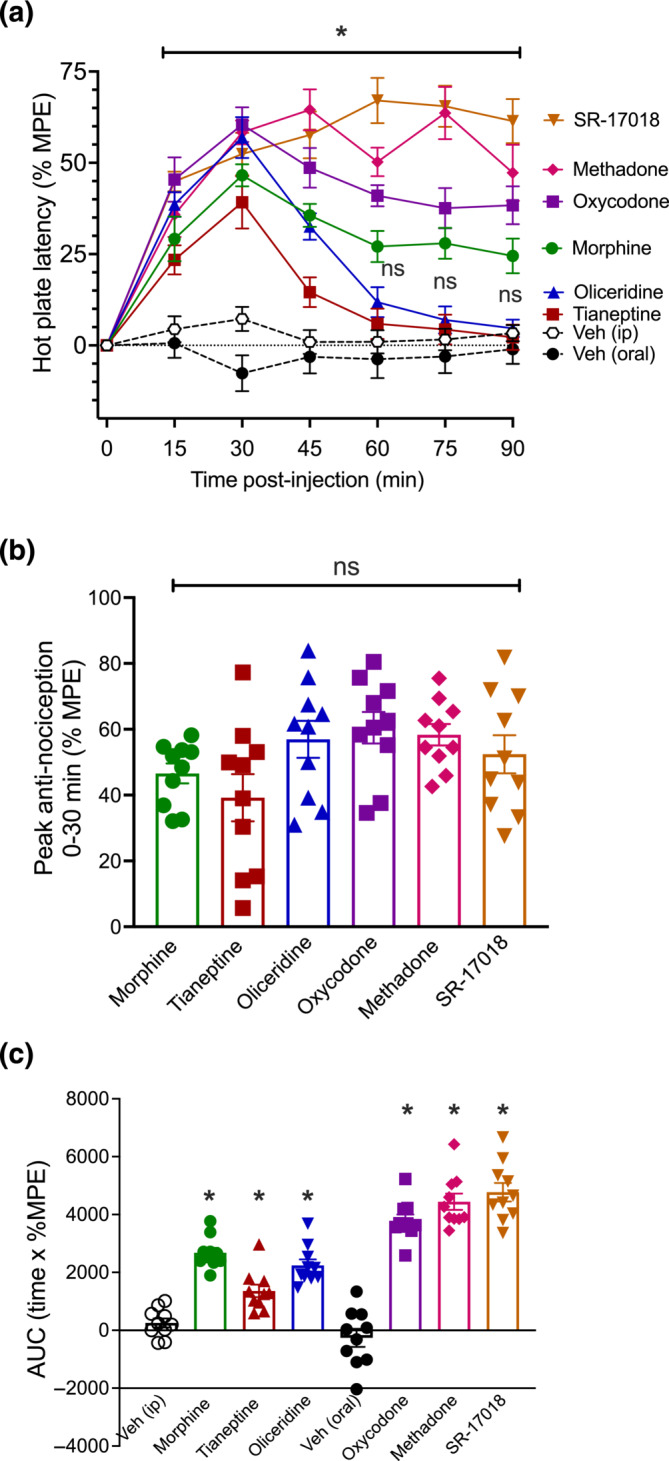
Equi‐effective respiratory doses of opioids and their induction of anti‐nociception in mice. (a) Morphine (3.44 mg·kg−1), tianeptine (12.74 mg·kg−1), oliceridine (0.745 mg·kg−1), oxycodone (0.71 mg·kg−1), methadone (2.5 mg·kg−1) and SR‐17018 (0.66 mg·kg−1) all induced significant anti‐nociception. Data shown are means ±SEM. n = 10 for all groups. *P < 0.05, significantly different as indicated. The effect of tianeptine and oliceridine was not significantly different from vehicle after 60 min (ns); two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's comparison. (b) No statistical difference was detected at 30‐min post‐injection across the six opioids. (c) Area under the curve (AUC) analysis of data in (a) showed induction of anti‐nociception by all opioids, relative to their corresponding vehicle. In (b, c), data shown are individual values with means ±SEM; n = 10 for all groups. *P < 0.05, significantly different from vehicle (Veh) control; ns indicates non‐significant; one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's comparison. Statistical test details are provided in Table S2.
