FIGURE 1.
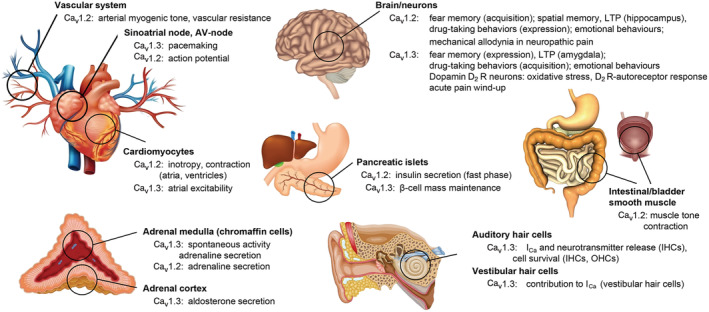
Physiological roles for Cav1.2 and Cav1.3 L‐type Ca2+‐channels (LTCCs). Cav1.2 and Cav1.3 are expressed in most excitable tissues and in most cases even together in the same cells. They can support different physiological functions due to their distinct gating properties (Cav1.3 channels are ‘low‐voltage‐activated LTCCs’), subcellular localization and/or protein‐interactions. Cav1.1 and Cav1.4 show more restricted expression in skeletal muscle and retinal cells and serve key functions for skeletal muscle contraction and photoreceptor signalling, respectively (Zamponi et al., 2015). AV‐node, atrioventricular node; ICa, inward Ca2+ current, IHC, inner hair cells; LTP, long‐term potentiation; OHC, outer hair cells. Adapted from Zamponi et al. (2015), redrawn with permission.
