FIGURE 2.
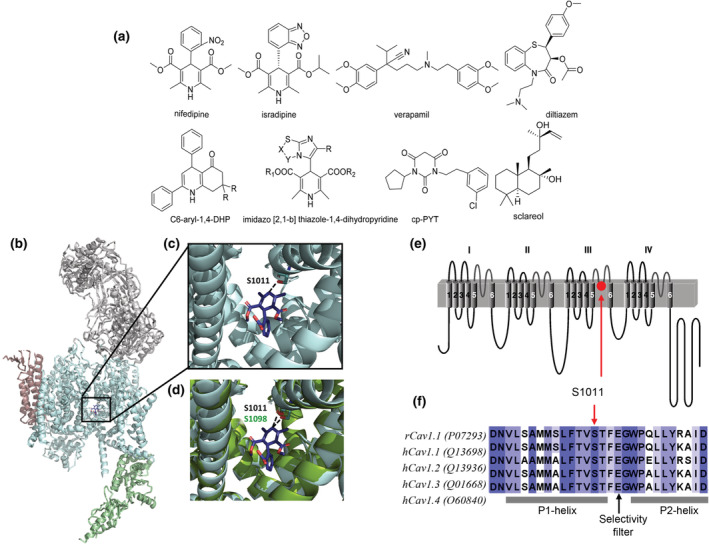
Chemical structures of compounds discussed in this article and L‐type Ca2+‐channel (LTCC) structure. (a) Isradipine (previously also referred to as PN200‐110) is shown as its active (S)‐(+)‐enantiomer, diltiazem as its active (+)‐cis‐diastereomer. Other names that can be found in the literature for cp‐PYT (1‐(3‐chlorophenethyl)‐3‐cyclopentylpyrimidine‐2,4,6‐(1H,3H,5H)‐trione) are compound 8 and BPN‐4689. (b) The structure of the rabbit Cav1.1 channel complex with nifedipine bound in the DHP binding pocket (PDB entry 6JP5 Zhao et al., 2019). α1, β, γ and α2δ1 subunits are coloured pale cyan, pale green, brown and grey, respectively. The DHP blocker nifedipine is shown in dark purple. Lipids facing the DHP binding‐site has been removed for clarity. (c) DHP‐binding site in the Cav1.1 structure with serine residue 1011 (numbering according to rabbit rCav1.1 α1‐sequence, Uniprot P07293) indicated. (d) Homology model of human hCav1.3 α1‐subunit (Uniprot Q01668) based on the rCav1.1 structure, generated with MOE (Molecular Operating Environment, version 2020.09, Molecular Computing Group Inc., Montreal, Canada). The hCav1.3 α1‐subunit (dark green) is shown in comparison to Cav1.1 (pale cyan). The serine residue (corresponding to S1098 in hCav1.3) represents the hydrogen‐bond acceptor partner of the hydrogen‐bond donor‐NH group in the DHP‐ring. This hydrogen bond is critical for the channel‐gating modifying activity of DHPs. (e) For orientation, the schematic transmembrane topology of Cav α1‐subunits is shown to highlight the approximate position of serine 1098 (red circle) in the P1 helix of repeat III in Cav1.3 α1. F. S1011 is highly conserved in all LTCCs and located close to one of the negative charges forming the channel's selectivity filter.
