Figure 3.
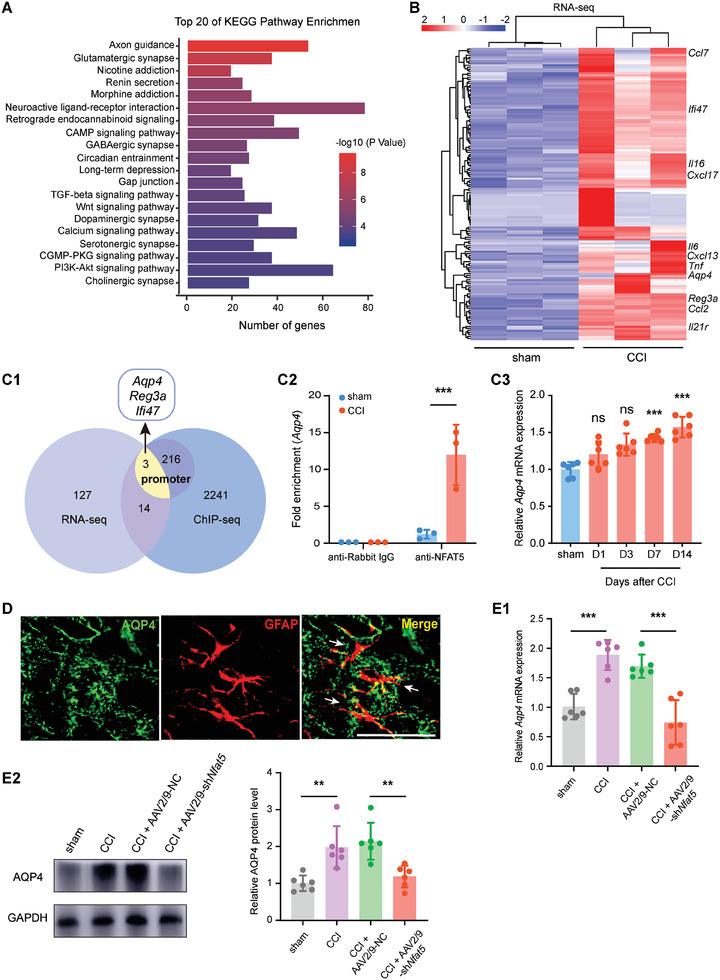
NFAT5 regulates AQP4 expression. A) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis of ChIP‐seq of NFAT5 targets. B) Heat map showed 144 significantly up‐regulated genes in the SDH of CCI group rats compared with the sham group by RNA‐seq analysis. C1) The intersection of NFAT5 ChIP‐seq data with RNA‐seq data from sham and CCI groups. C2) ChIP‐qPCR analysis of endogenous NFAT5 binding at Aqp4 promoters in the SDH after CCI. ***p < 0.001, n = 3, two‐tailed unpaired Student's t‐test. C3) Expression of Aqp4 mRNA in the injured ipsilateral SDH after sham or CCI surgery. Compared to the sham‐operated rats, ***p < 0.001, n = 6, one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. D) Immunofluorescence double‐labeling of AQP4 (green) and astrocyte marker GFAP (red) in the SDH on day 7 after CCI modeling. Scale bar = 100 µm. E1) Aqp4 mRNA expression after i.t. administration of AAV2/9‐shNfat5 in the SDH of CCI rats. CCI versus sham, ***p < 0.001, CCI + AAV2/9‐shNfat5 versus CCI + AAV2/9‐NC, ***p < 0.001, n = 6, one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. E2) AQP4 protein expression after i.t. administration of AAV2/9‐shNfat5 in the SDH of CCI rats. CCI versus sham, **p < 0.01, CCI + AAV2/9‐shNfat5 versus CCI + AAV2/9‐NC, **p < 0.01, n = 6, one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test.
