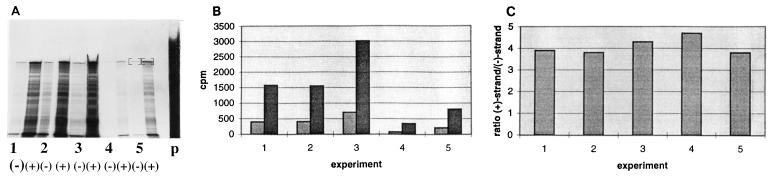
FIG. 4.
Determining the ratio of positive-strand RNA to negative-strand RNA in DI9c-transfected cells. BHK-21 cells were transfected in five independent experiments with DI9c, and the cytoplasmic RNA was extracted and subjected to an RNase protection assay 24 h p.t. To facilitate quantitation, positive and negative strands were both assayed with the same antisense probe, the latter by detection of positive strands which were protected by equimolar amounts of negative strands in a prehybridization-predigestion cycle (see Materials and Methods and Results). (A) The protected fragments were separated on a 10% polyacrylamide–7 M urea gel. p, amount of input probe that (with respect to the viral RNA) was added in excess into each protection assay mixture. (−), detected negative-strand RNA; (+), detected positive-strand RNA. (B) The major bands on the gel were extracted (indicated in panel A, lanes 5) and quantified by Cerenkov counting. Light grey columns represent the amounts of protected negative-strand RNA; dark grey columns represent the amounts of protected positive-strand RNA. (C) The ratio of positive-strand RNA to negative-strand RNA was calculated for each of the five experiments.