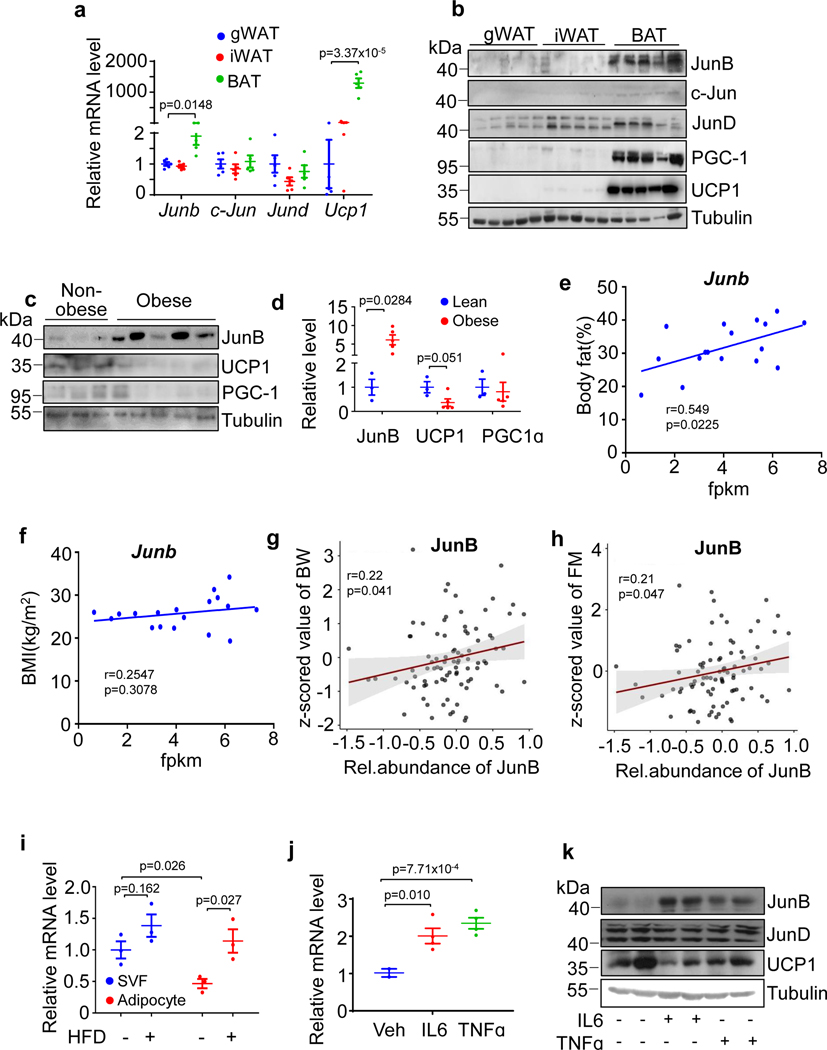
Fig. 1 |. JunB expression in thermogenic fat is positively correlated with obesity.
a,b, mRNA (n = 6 mice per group) (a) and protein (n = 5 mice per group) (b) levels of JunB, Jun, JunD and UCP1 in gWAT, iWAT and BAT of 10-week-old male mice. c, JunB protein expression was induced in the deep neck fat of obese individuals (n = 3 (non-obese), n = 5 (obese)). d, The quantified data of JunB expression in c. e,f, The mRNA levels of JunB in human deep neck fat were positively correlated with body fat (%) (e) and BMI (f). g,h, Protein levels of JunB in brown fat were positively correlated with body weight (BW) (g) and fat mass (FM) (h) in rodents. i, mRNA levels of JunB in the BAT fractions of adipocytes and SVFs were enhanced in diet-induced obesity (n = 3 mice per group). j,k, Expression levels of JunB in mRNA (n = 3, independent experiments) (j) and protein (n = 4, independent experiments) (k) were induced by the treatment of 20 ng ml−1 IL-6 or 20 ng ml−1 TNF for 24 h in day-6 differentiated brown adipocytes. The loading control tubulin in one membrane was used as the processing control for different gels with identical loading volumes for the sample in b and k. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. Statistical analysis was performed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient (d–h) and an unpaired two-sided t-test. FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads.