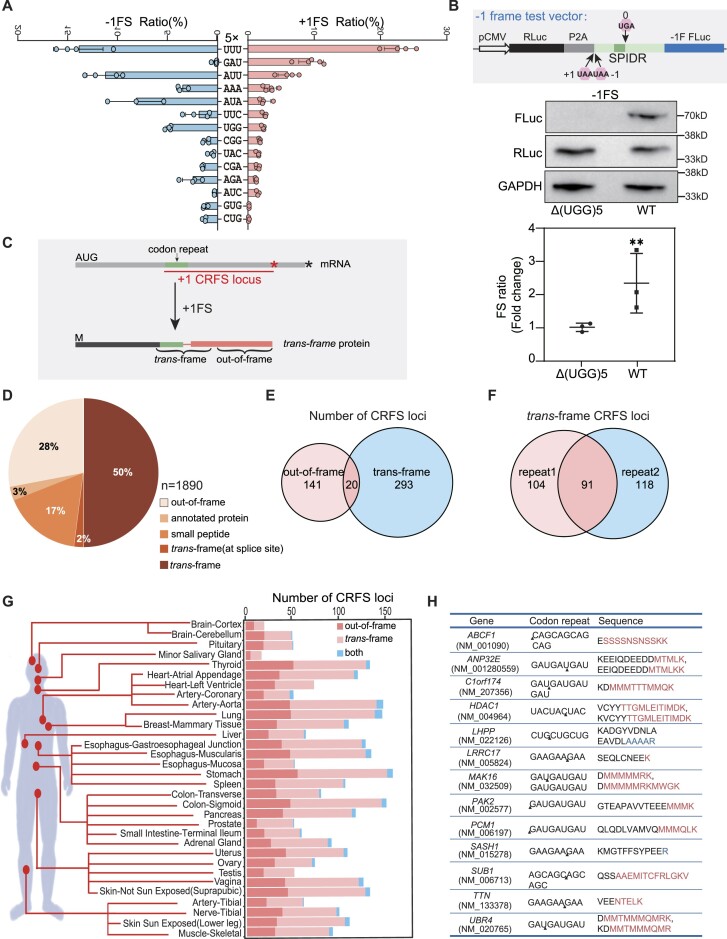
Figure 2.
Codon repeat-induced ribosomal frameshifting may widely occur in humans. (A) Frameshifting ratio determined by the P2A dual luciferase system from different types of codon repeat (5-time repeats) in HEK293T cells. Error bars, standard deviation of 3 biological repeats. (B) Detection of ribosomal frameshifting of (UGG)5 in the SPIDR gene. Diagram (top) shown the structure of the construct, with the dark green box indicating the position of (UGG)5 repeats. Middle and bottom panel showing the western blot result and luciferase activity assay. Three biological replicates were analyzed for each experiment. Error bars, standard deviation. (**) P < 0.01 (Student's t-test). (C) Diagram illustrating the definition of CRFS locus, trans-frame peptide and out-of-frame peptide in the trans-frame protein. Red and black asterisk mean the position of first stop codon in the +1 and 0 frame, respectively. (D) Pie chart showing the distribution of peptides detected in human tissue proteomes. Trans-frame or out-of-frame were defined in (C). Annotated protein means peptide sequences match unexpressed annotated proteins. Small peptide means sequences match the smProt database. Splice site means trans-frame peptides positioned at splicing junctions. (E) Venn diagram showing the number of CRFS loci supported by trans-frame, out-of-frame peptides or both. (F) Venn diagram showing the number of CRFS loci supported by trans-frame peptides detected in proteomic data of each biological repeats. (G) Diagram showing the number of CRFS loci supported by unique trans-frame and/or out-of-frame peptides from proteomic data of 32 human tissues. (H) Unique trans-frame peptides detected in two biological repeats and represented in > 16 human tissues. Red sequences are encoded by +1 frame, blue by −1 frame, and black by 0 frame.