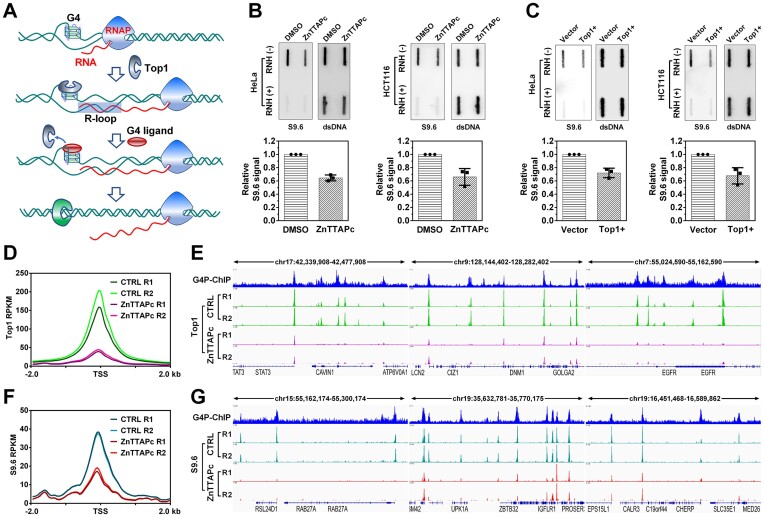
Figure 6.
ZnTTAPc releases Top1 trapped by chromosome G4 and reduces intracellular R-loop levels. (A) Illustration of the interaction between G4, G4 ligand, Top1 and R-loop. Transcription-induced negative supercoiling on DNA strands promotes the formation of G4 structures and R-loops. Top1 becomes trapped by G4 and loses its ability to relax the negatively supercoiled DNA. Displacing Top1 on G4 using a G4 ligand allows it to relax the DNA, thereby inhibiting R-loop formation. (B) Detection of R-loop in the genomic DNA from HeLa and HCT116 cells treated or untreated with 10 μM ZnTTAPc using slot blot. R-loop levels were quantified and normalized by calculating the ratio of signals obtained from the R-loop-specific antibody (S9.6) and the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibody. (C) Detection of R-loop on genomic DNA from HeLa and HCT116 cells transfected with a plasmid encoding the Top1 gene (Top1+) or an empty control vector, using slot blot analysis. (D) Top1 distribution around the transcription start sites (TSS) of genes. Top1 binding sites were identified in the chromosomes of HCT116 cells, treated or untreated with 10 μM ZnTTAPc, using the CUT&Tag assay. (E) Examples of specific G4 formation sites (G4P-ChIP) and Top1 binding sites in the chromosomal DNA of HCT116 cells. (F) R-loop distribution around TSS in genes. R-loops were detected in the chromosomes of HCT116 cells, treated or untreated with 10 μM ZnTTAPc, using the CUT&Tag assay. (G) Examples of G4 (G4P-ChIP) and R-loop formation sites in the chromosomal DNA of HCT116 cells.