Fig. 1.
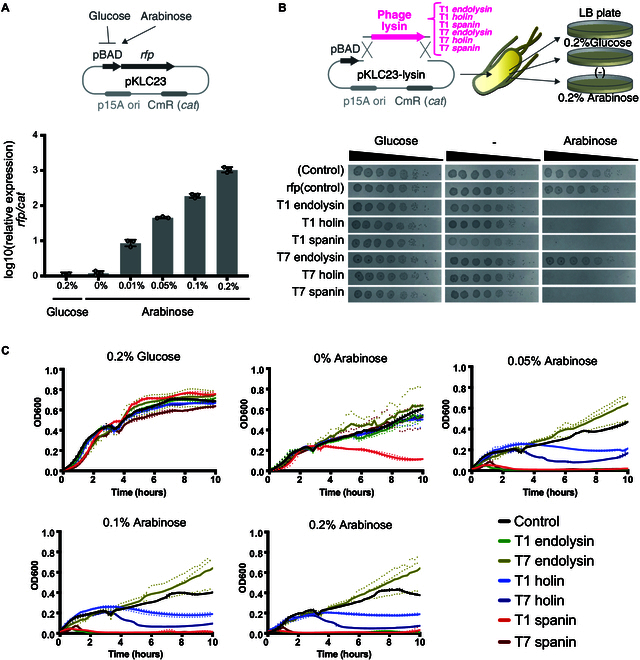
Comparison of bactericidal activity of lysins from bacteriophages. (A) Expression efficiency of genes under the control of the arabinose promoter. E. coli MC1061 harboring arabinose-inducible rfp expression plasmid (pKLC23) was cultured in LB+Cm medium containing glucose or arabinose. mRNA was extracted and expression of the rfp gene was measured using real-time PCR. The data are the means ± standard deviations based on 3 wells per group. (B) Spot test to quantitatively assess the bactericidal activity of phage-derived lytic enzymes. E. coli MC1061 harboring pKLC23 plasmid expressing lytic enzymes (endolysin, holin, or spanin) derived from T1 or T7 bacteriophages under the control of an arabinose-inducible promoter grown in LB+Cm+glucose (0.2 wt%) medium were serially diluted from 10−1 to 10−7 using LB+Cm medium. Four microliters of each dilution was spotted onto LB+Cm+glucose (0.2 wt%), LB+Cm, and LB+Cm+arabinose (0.2 wt%) plates. Spot tests were performed using 4 clones in each E. coli MC1061 strain. The photograph shown is the representative data. All assays were replicated 3 times. (C) Growth curves of the E. coli MC1061 harboring plasmid expressing lytic enzymes under the control of an arabinose-inducible promoter. Bacteria were cultured in LB medium with a glucose concentration of 0.2 wt% or arabinose with a concentration of 0 wt% to 0.2 wt%. The optical density (OD600) was measured every 10 min for 10 h. The experiment was conducted using 3 independent bacterial cultures (represented by dashed lines), and the average values were plotted as solid lines. Abbreviations: Cm, chloramphenicol; LB, Luria-Bertani medium.
