Fig. 2.
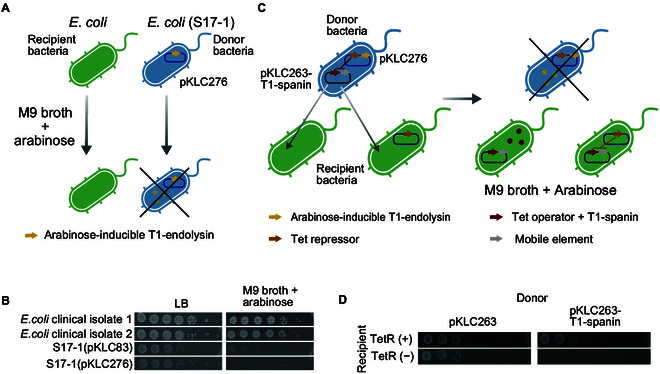
Development of a method to investigate bactericidal activity of target genes using conjugation. (A) Schematic diagram of a selective killing method for the donor strain Escherichia coli S17-1, using M9 minimal broth and T1-endolysin. (B) Selective killing of the donor strain S17-1. Clinical isolates of E. coli, and the donor strains, E. coli S17-1(pKLC83) or E. coli S17-1(pKLC276 [arabinose-inducible endolysin]), were spotted onto agar plates containing LB medium or M9 minimal broth supplemented with 0.2 wt% arabinose. (C) Illustration of a conjugation system used to assess the bactericidal activity of T1-spanin. The donor E. coli strain S17-1 (blue) carries a Tet repressor expression plasmid (required for suppressing the expression of T1-spanin within the donor E. coli) and a T1-spanin expression plasmid. Through conjugation, the mobile T1-spanin expression plasmid is transferred to recipient bacteria (green). The mixed bacteria are cultured on the agar plate containing M9 minimal medium supplemented with arabinose, leading to the killing of the donor bacteria. T1-spanin is expressed in recipient cells that do not express the Tet repressor. (D) Recipient bacteria, expressing the Tet repressor encoded by pKLC83, received a tetracycline-inducible T1-spanin expression plasmid (pKLC263-T1-spanin) through conjugation. The bacterial culture was spotted onto agar plates containing M9 minimal medium supplemented with arabinose. The photograph shows representative data. All assays were performed in triplicate. Abbreviation: LB, Luria-Bertani medium.
