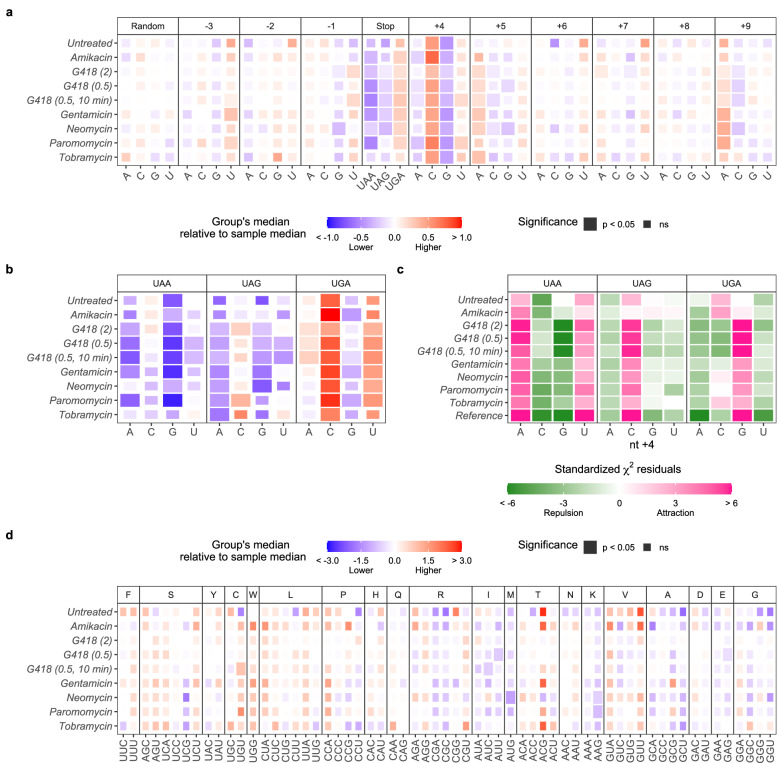
Fig. 2. Effects of the stop codon and flanking nucleotide identities on readthrough efficiency.
a, b, d Differences between median readthrough efficiency of all mRNAs in the sample and median readthrough efficiency of a group of mRNAs containing particular stop codon or nucleotide (a), stop codon with nt +4 as quadruplet (b), or triplet codon in the ribosomal P-site (d). Positive (red) and negative (blue) values indicate that the group of mRNAs had higher and lower median readthrough efficiency compared to the sample median, respectively. Two-tailed Wilcoxon’s rank sum test with the Benjamini–Hochberg method for multiple testing correction was used to determine whether the difference was significant. c Standardized residuals of two-tailed χ2 test of independence determining association between stop codon and nt +4 identities. Positive residuals (pink) indicate that the pair occurs together more often than expected (attraction), while negative residuals (green) are less often than expected (repulsion). For all panels, a significant result (p < 0.05) is represented as a larger tile. Source data, the exact p-values, and the number of data points (n) in each group are provided as a Source Data file.