FIGURE 5.
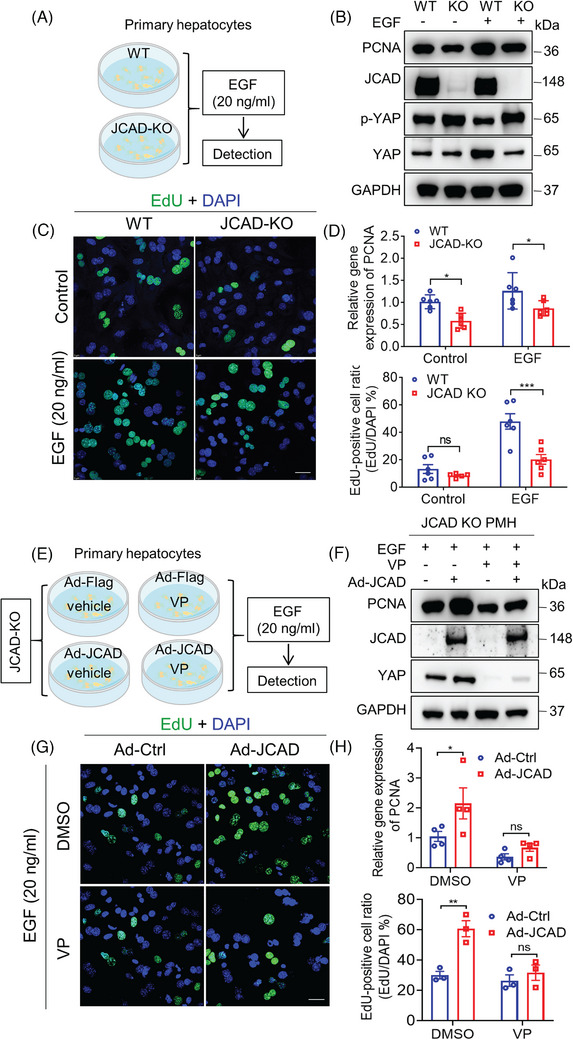
Junctional protein‐associated with coronary artery disease (JCAD) sensitised primary hepatocytes to epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation via Hippo signalling pathway. (A) Primary hepatocytes were isolated from wild‐type (WT) and JCAD knockout (JCAD‐KO) mice and stimulated with 20 ng/mL murine EGF for 24 h. (B) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), p‐YAP and Yes‐associated protein (YAP) protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis. (C) Less 5‐ethynyl‐2′‐deoxyuridine (EdU)‐positive cells were stained with or without EGF stimulation. Ratio of EdU‐positive cells was presented as EdU‐positive cells over 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI) per field (n = 6, two‐way analysis of variance [ANOVA] with Tukey's multiple comparisons). At least five fields were counted. (D) PCNA gene expression was less responding in JCAD‐KO hepatocytes with or without EGF (n = 6, two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons). (E) The cell‐processing flow diagram is described as follows. Primary hepatocytes were isolated from JCAD‐KO mice and infected with either control adenovirus (Ad‐Ctrl) or JCAD expressing adenovirus (Ad‐JCAD) for 48 h, at 24 h post infection, 20 ng/mL EGF with or without verteporfin (VP) (5 μM) was added for another 24 h. (F–H) VP abolished increased expression of PCNA and EdU incorporation induced by Ad‐JCAD infection (H, n = 4; G, n = 3, two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons). At least five images were taken for each treatment. Scale bars, 25 μm. Representative images were chosen from three independent experiments. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM), * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001 compared to control group.
