Fig. 2.
iPSCs containing novel GBE1 variant differentiate into hepatocytes and exhibit deficiency of GBE1 activity.
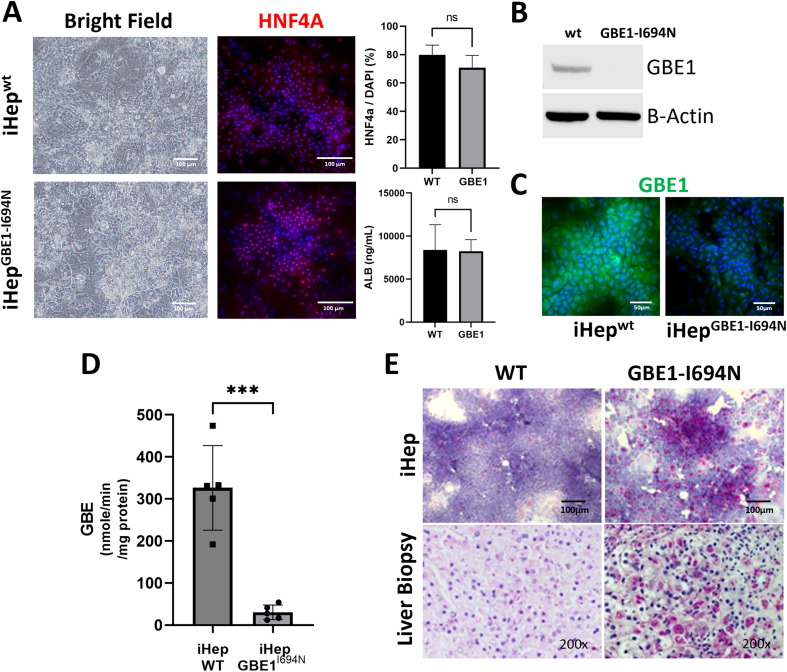
A) Brightfield microscopy and immunofluorescent staining of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha (HNF4a: red, Hoechst nuclear stain: blue) revealed comparable patterns in iHepwt and iHepGBE1-I694N. Additionally, there is no significant difference in albumin production in the culture supernatant (measured by ELISA) between iHepwt and iHepGBE1-I694N. Sample size: n = 5 each for HNF4a staining, WT n = 5 and mutant n = 6 for albumin production. Graphs were generated using Prism GraphPad 9.5.0. P values were determined using the two-tailed t-test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. B) Western blot analysis shows that GBE1 expression is comparable between iHepwt and iHepGBE1-I694N. Beta-actin is used as a loading control. C) GBE1 enzyme assay showed significantly reduced activity in iHepGBE1-I694N compared to iHepwt. n = 5 samples for both groups. ***: p = 0.001, using the two-tailed t-test. D) PAS-D staining revealed polyglucosan deposits in iHepGBE1-I694N, which correlates with the proband's liver biopsy. Both iHepwt and healthy liver tissue were negative for PAS-D staining. Liver biopsy image was taken on a scale of x200.