Figure 1.
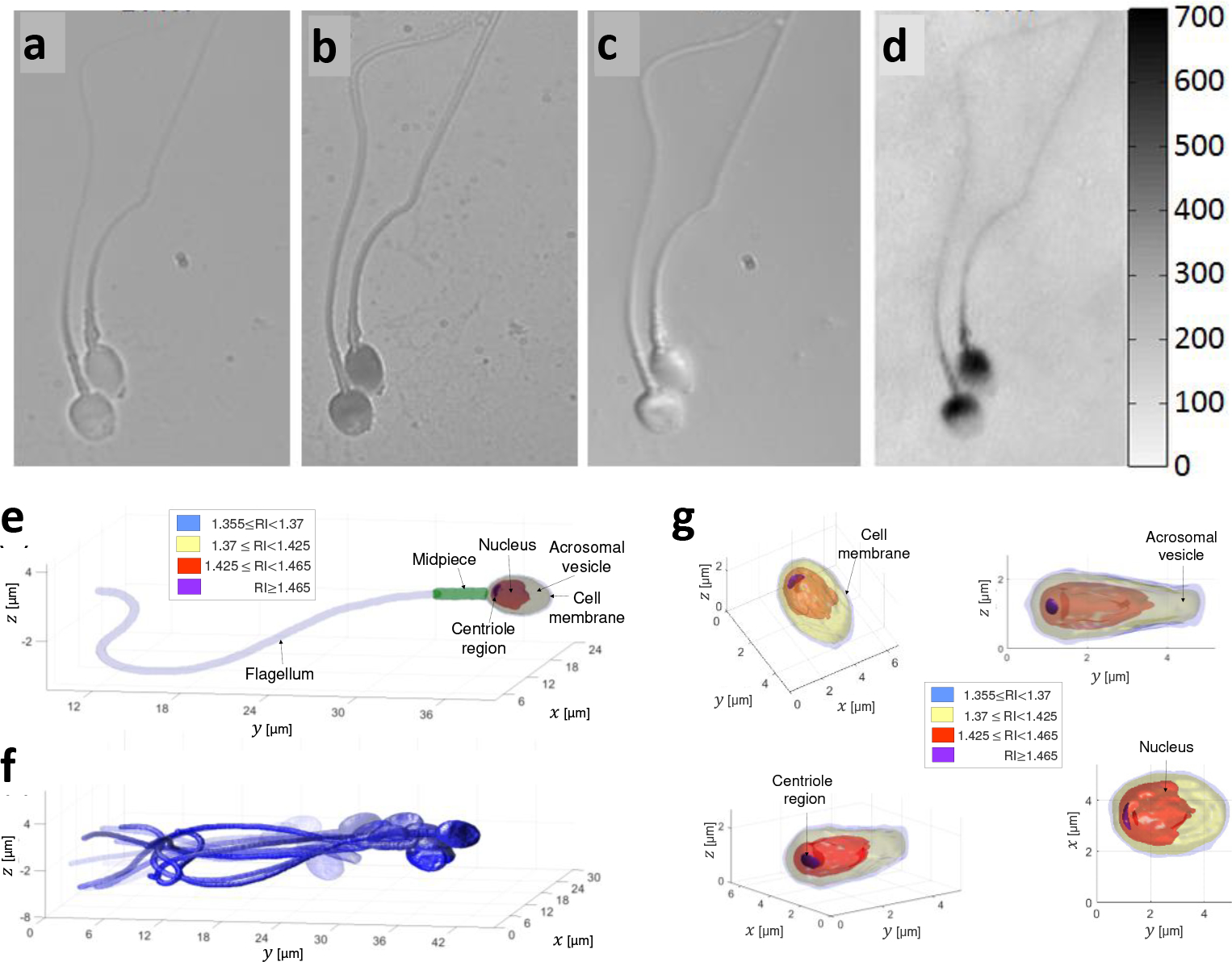
Comparison of imaging methods of human sperm cells. a, Label-free bright-field imaging, presenting low-contrast where the cell inner content cannot be seen. b, Label-based bright-field imaging (not allowed in human in-vitro fertilization). c, Label-free differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, a qualitative PhM method. d, Label-free quantitative PhM, where the colorbar on the right represents optical path delay values in nm.6 e-f, High-resolution label-free dynamic 3D imaging of a sperm cell swimming freely, acquired by interferometric computed tomography. Reproduced from Ref. 9. e, A single frame from the 3D motion, revealing the internal structure of the sperm cell. f, Overlay of 15 frames from the 3D motion. g, The sperm cell head 3D refractive-index profile from various perspectives. RI referred to refractive index.
