Figure 4. Sex differences in the effects of ethanol drinking and intermittent predator odor stress on glucocorticoid receptor (GR) protein levels in prefrontal cortex (PFC).
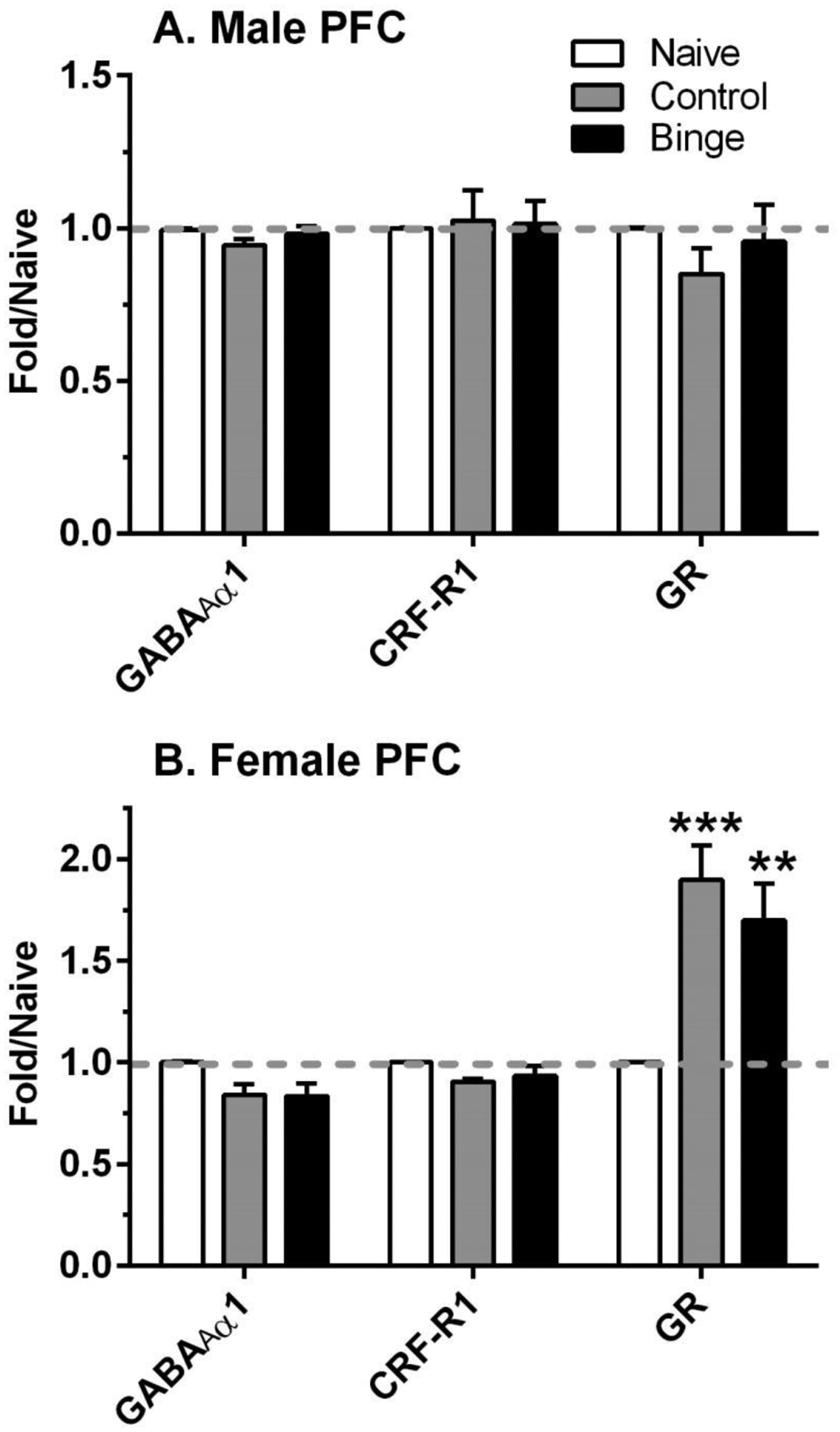
Western blot analysis was conducted on dissected PFC tissue at 24 h after the final lickometer session (binge = prior binge ethanol intake; control = prior water intake) and compared to values from similarly aged naïve mice (naïve). Divergent effects of treatment were observed on protein levels of GR in male and female PFC. Values are mean ± SEM for each group; in some cases, SEM is contained within the mean: male: n=6–10 (naïve), n=11 (control), n=12 (binge); female: n=6–9 (naïve), n=8 (control), n=9–11 (binge). All levels were initially normalized to β-actin. Fold regulation was then determined by normalizing individual values to the mean of the relative expression of the respective naïve group (dashed gray line). **p<0.01, ***p=0.001 vs respective naïve. GABAAR α1 = GABAA receptor α1 subunit; CRF-R1 = corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1
