Figure 4. LA regulates histone H3K27 acetylation to inhibit pro-inflammatory response in macrophages.
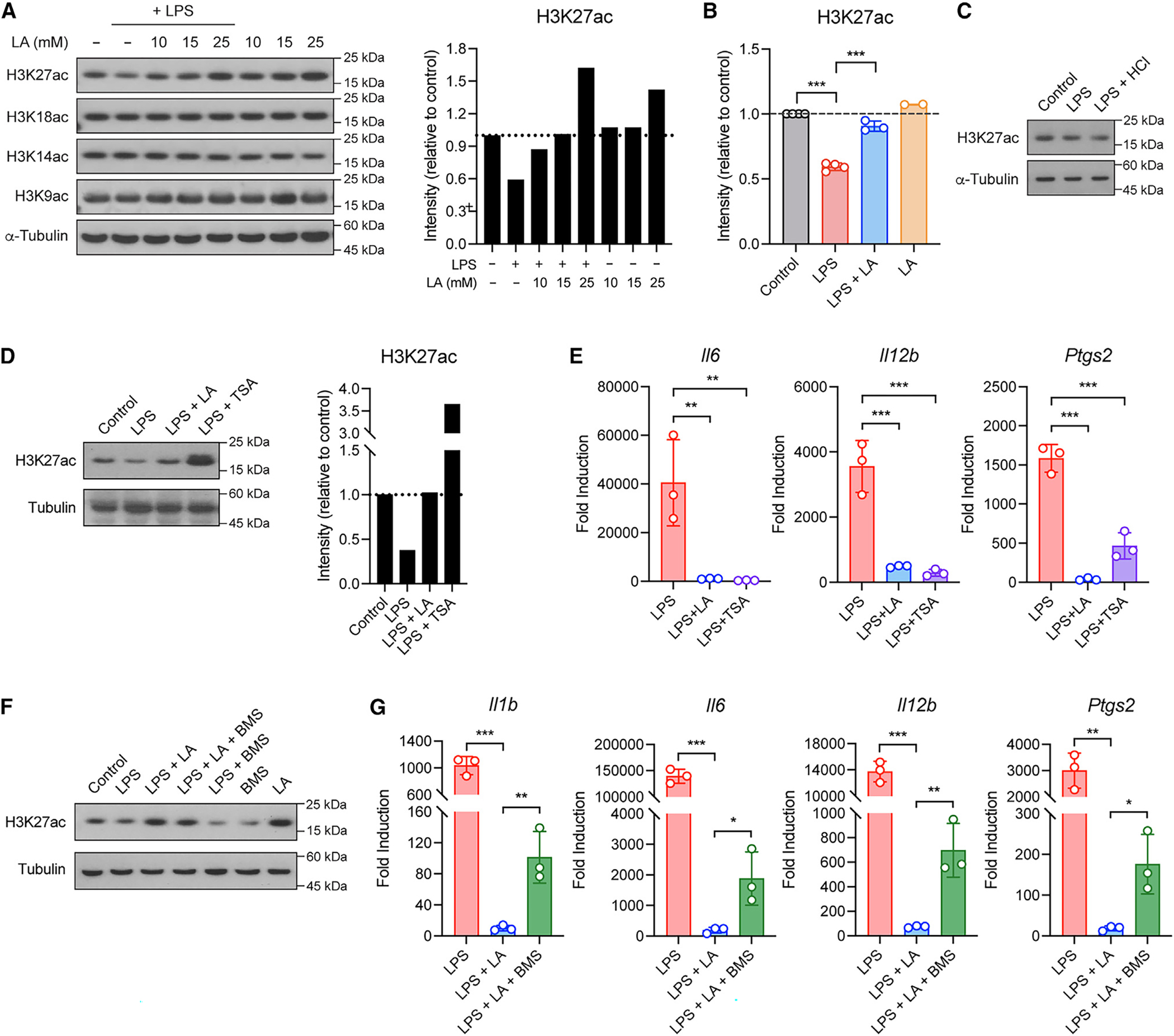
(A and B) Global histone acetylation in BMDMs stimulated without or with LPS in the presence or absence of LA at the indicated concentrations (A) or 10 mM (B). Shown in (A, right) and (B) are quantified signals for histone H3K27 acetylation.
(C) Global histone H3K27 acetylation in BMDMs stimulated without (control) or with LPS in normal or low-pH condition with HCl.
(D) Global histone H3K27 acetylation in BMDMs stimulated without (control) or with LPS in the presence or absence of TSA. Shown in the right are quantified signals for histone H3K27 acetylation.
(E) Pro-inflammatory gene expression in BMDMs stimulated as in (D).
(F) Global histone H3K27 acetylation in BMDMs stimulated without (control) or with LPS in the presence or absence of BMS.
(G) Pro-inflammatory gene expression in BMDMs stimulated as in (F). Data are mean ± SD of two to four independent experiments (B) or triplicates of representative experiments (E and G). One-way ANOVA (B, E, and G) followed by Tukey’s post-test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.001.
