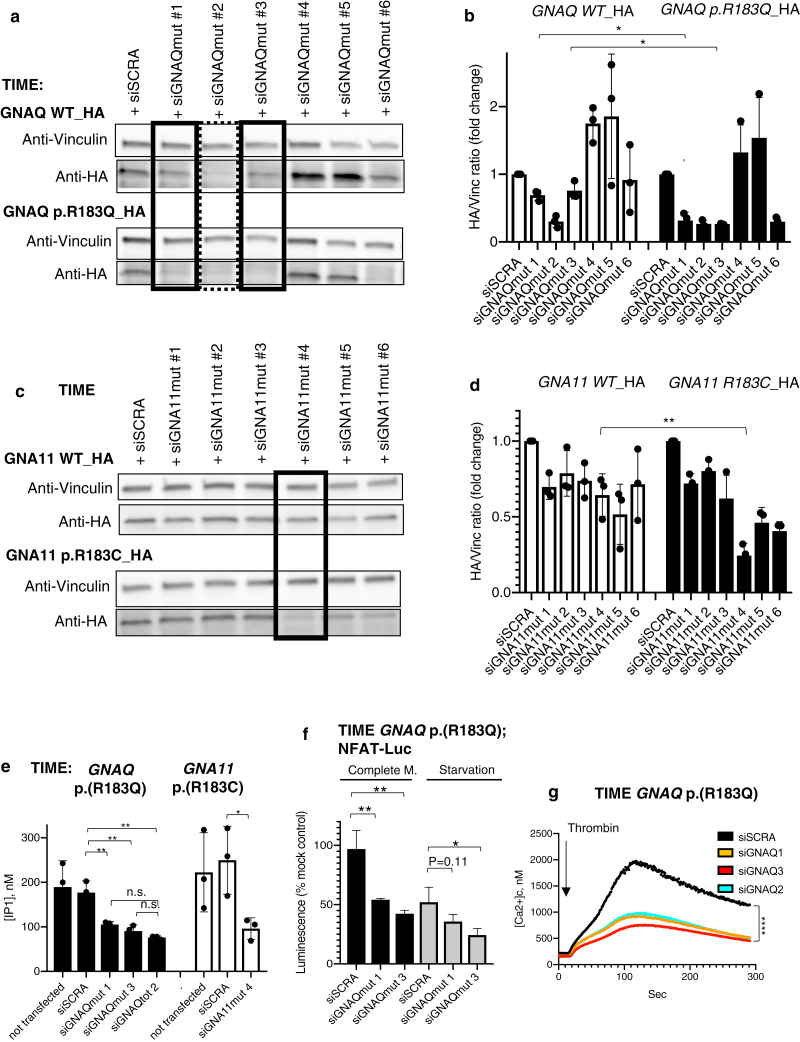
Figure 2.
Identification of siRNAs for specific targeting of GNAQ or GNA11 variant alleles leads to rescue of aberrant calcium signaling in variant cells. (a) TIME cells stably expressing either WT or p.(R183Q) HA-tagged Gaq were transfected by 50 nM siRNAs targeting GNAQ c.548G > A, p.(R183Q) allele and analysed by western blot 24 hours after transfection. Lysates were probed with the indicated antibodies. siRNAs siGNAQmut #1 and 3 (squared with solid lines) showed specific knockdown of variant protein over WT counterparts. siRNA siGNAQmut #2 (dotted square) knockeddown both variant and WT proteins. (b) Densitometric quantification of bands from western blot experiments similar to the ones shown in Figure 2a (mean ± SD of three experiments, ∗ P < .05). (c) TIME cells stably expressing either WT or p.(R183C) HA-tagged Ga11 were transfected by 25 nM siRNAs targeting GNA11 c.547C > T, p.(R183C) allele and analysed by western blot 24 hours after transfection. Lysates were probed with the indicated antibodies. siRNAs siGNA11mut#4 (squared) showed specific knockdown of variant protein over WT counterparts. (d) Densitometric quantification of bands from western blot experiments similar to the ones shown in Figure 2c (mean ± SD of three experiments, ∗ P < .05). (e) TIME-GNAQR183Q or -GNA11R183C were not transfected or transfected with 25 nM nontarget siRNAs (siSCRA), 25 nM siRNAs for specific silencing of the variant alleles (siGNAQmut 1 and siGNAQmut 3 for targeting of GNAQ variant allele and siGNA11mut 4 for silencing of GNA11 variant allele), or 25 nM siRNA targeting both variant and WT GNAQ alleles (siGNAQ tot 2). IP1 concentration was measured 48-hours after transfection and shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical comparisons were performed by two-tailed unpaired t-test (∗∗P < .01, n.s.= nonsignificant). (f) TIME cells harbouring the GNAQR183Q variant were transfected with NFAT-luciferase reporter and a stable clone was obtained after antibiotic selection. TIME-GNAQ p.(R183Q); NFAT-Luc were transfected with nontarget siRNA (siSCRA) or two siRNAs for specific silencing of the variant GNAQ allele (siGNAQmut 1 and 3) and luciferase reporter activity was measured 48-hours after transfection in complete medium or after four hours of starvation, shown as mean ± SD of percentage change of cells transfected with mock in three independent experiments. Statistical comparisons were performed by two-tailed unpaired t-test (∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01). (g) TIME cells harbouring GNAQR183Q were transfected with nontarget siRNA (siSCRA), two siRNAs for specific silencing of the variant GNAQ allele (siGNAQ1 and siGNAQ3), or siRNA targeting both variant and WT GNAQ alleles (siGNAQ2). Forty-eight hours after transfection they were loaded with Fluo-8 intracellular calcium dye and stimulated by thrombin 1U/ml while recording fluorescent signal at 1 second intervals for up to 300 seconds. The graph shows the average of three independent experiments. Statistical tests performed by one-way ANOVA (∗∗∗∗P < .0001). AUC, area under curve; ERK, extracellular signal–regulated kinase; HA, hemagglutinin; HEK, human embryonic kidney; IP1, inositol-1-phosphate; mut, mutated; n.s., nonsignificant; pERK, phosphorylated ERK; siRNA, small interfering RNA; siSCRA; nontarget siRNA; TIME, telomerase-immortalised microvascular endothelial; WT, wild type.