Figure 4.
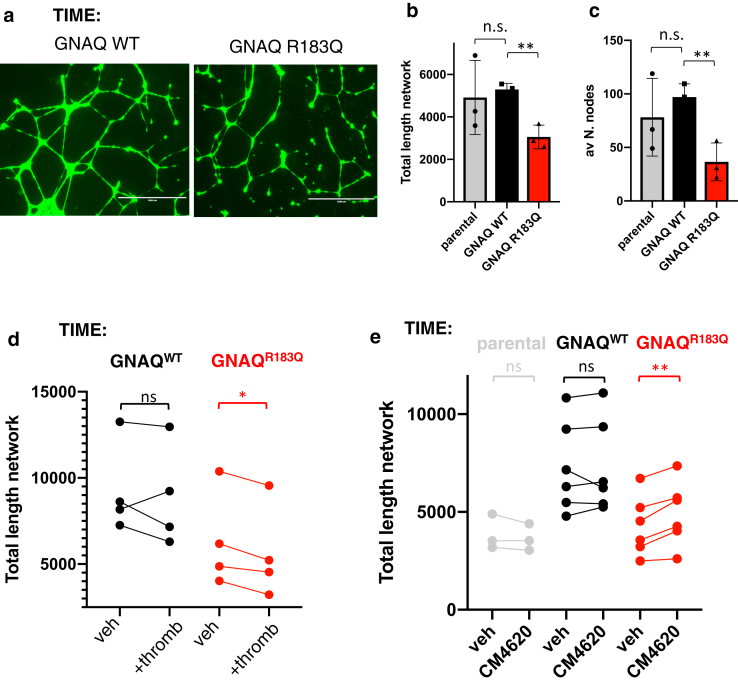
In vitro angiogenesis is disrupted by variant GNAQ and improved by CRAC inhibition. (a) Representative images captured with EVOS Floid Imaging System after Calcein AM staining during in vitro endothelial cell tube formation of TIME cells stably expressing either GNAQ WT or GNAQ R183Q. (b and c) Quantification of angiogenesis assays (average of three independent experiment, mean ± SD) demonstrates significant difference between WT and variant cells in total length of the network (defined as combined lengths of segments, branches, and isolated elements) (b) and in the average number of nodes in the network (c). Statistical significance calculated using two-tailed unpaired t-test on three independent experiments (∗∗P = .0035 in b, ∗∗P = .0083 in (c). (d) Quantification of angiogenesis assays (total length of the network, defined as combined lengths of segments, branches, and isolated elements, four experiments) demonstrates significant difference between vehicle and thrombin (0.3U/Ml)–treated TIME GNAQR183Q, but no statistically significant difference for TIME GNAQWT. Results shown as mean of a technical triplicate for each of 4 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed paired t-test on four independent experiments (n.s. = not significant, ∗P = .0125). (e) Quantification of angiogenesis assays (total length of the network, defined as combined lengths of segments, branches, and isolated elements, three experiments) performed in presence of thrombin 0.3U/Ml demonstrates significant difference between vehicle and CM4620 (1 mM)–treated TIME GNAQR183Q, but no statistically significant difference for parental or GNAQWT TIME. Results shown as three or six independent experiments, and statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed paired t-test (n.s. = statistically nonsignificant, ∗∗P = .0048). n.s., nonsignificant; TIME, telomerase-immortalised microvascular endothelial; WT, wild type.