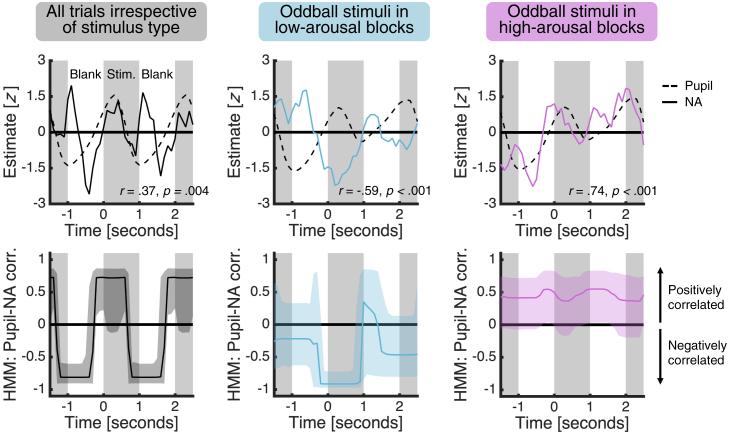
Figure 4.
Coupling between pupil and NA estimates varies with emotional arousal
The panels show (top) the average estimated pupil and NA time series with simple correlation statistics reported and (bottom) the HMM estimate of pupil-NA coupling for (left) all trials irrespective of stimulus type, (middle) oddball stimuli in low-arousal blocks, and (right) oddball stimuli in high-arousal blocks. We first smoothed the time series using a 0.5 s causal filter and Z scored the smoothed data for each trial. We then averaged the time series for each condition, removed any linear drift, and scaled the average time series to have unit variance, by dividing each time point by the average of the condition-specific standard deviations over the average time series. The last step helps ensure that estimated correlations, which are sensitive to the variance of the data, are comparable across conditions. Shaded area for the HMM estimate of pupil-NA coupling indicates 95% credible interval. See Figure S4 for simple correlations for oddball stimuli in each block.