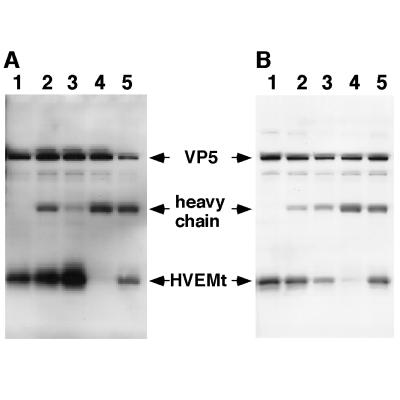
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of HSV-1 binding to HVEMt by Abs specific for HSV envelope glycoproteins. Gels in panels A and B represent two separate experiments carried out in the same way. Purified HSV-1 KOS virions (107 PFU) were preincubated for 1 h at 37°C with the following Abs or left untreated (−). The Abs specific for gB were SS10 (0.5 μl of ascites), DL16 (5 μg of IgG), DL21 (5 μg of IgG), and R69 (0.5 μl of sera) (lane 2). The Abs specific for gC were MP1 (0.5 μl of ascites), MP5 (5 μg of IgG), 1C8 (5 μg of IgG), and R46 (0.5 μl of sera) (lane 3). The Abs specific for gD were 1D3 (0.5 μl of ascites), DL2 (5 μg of IgG), DL11 (5 μg of IgG), and R7 (0.5 μl of sera) (lane 4). The Abs specific for gH/gL were LP11 (0.5 μl of ascites), 53S (5 μg of IgG), H6 (5 μg of IgG), and R137 (0.5 μl of sera) (lane 5). Samples were then subjected to sedimentation with HVEMt as described in the legend to Fig. 1. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (12% polyacrylamide) followed by Western blotting with anti-VP5 and anti-HVEM polyclonal Abs. Secondary Abs were then added, and enhanced chemiluminescence was used to visualize the bands.