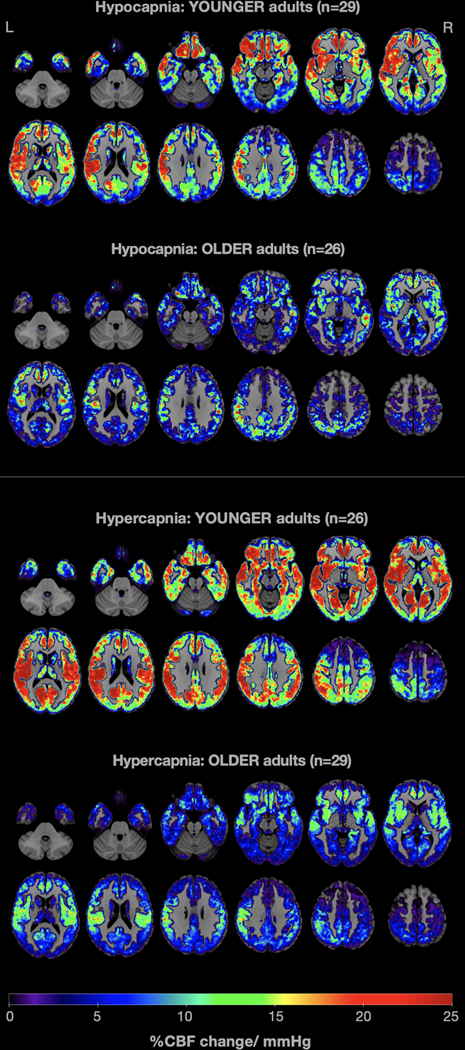
Fig. 3.
Average whole-brain gray-matter cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) maps contrasting young and older adults in 0.1Hz paced breathing (top: hypocapnia) and breath hold (bottom: hypercapnia) conditions. CVR was computed as the percent change in CBF per mmHg change in etCO2. Warm colors indicate higher CVR values, while cold colors show lower CVR values. It is easily noticeable that older adults demonstrated attenuated CVR in both conditions, compared with younger adults.