Figure 1.
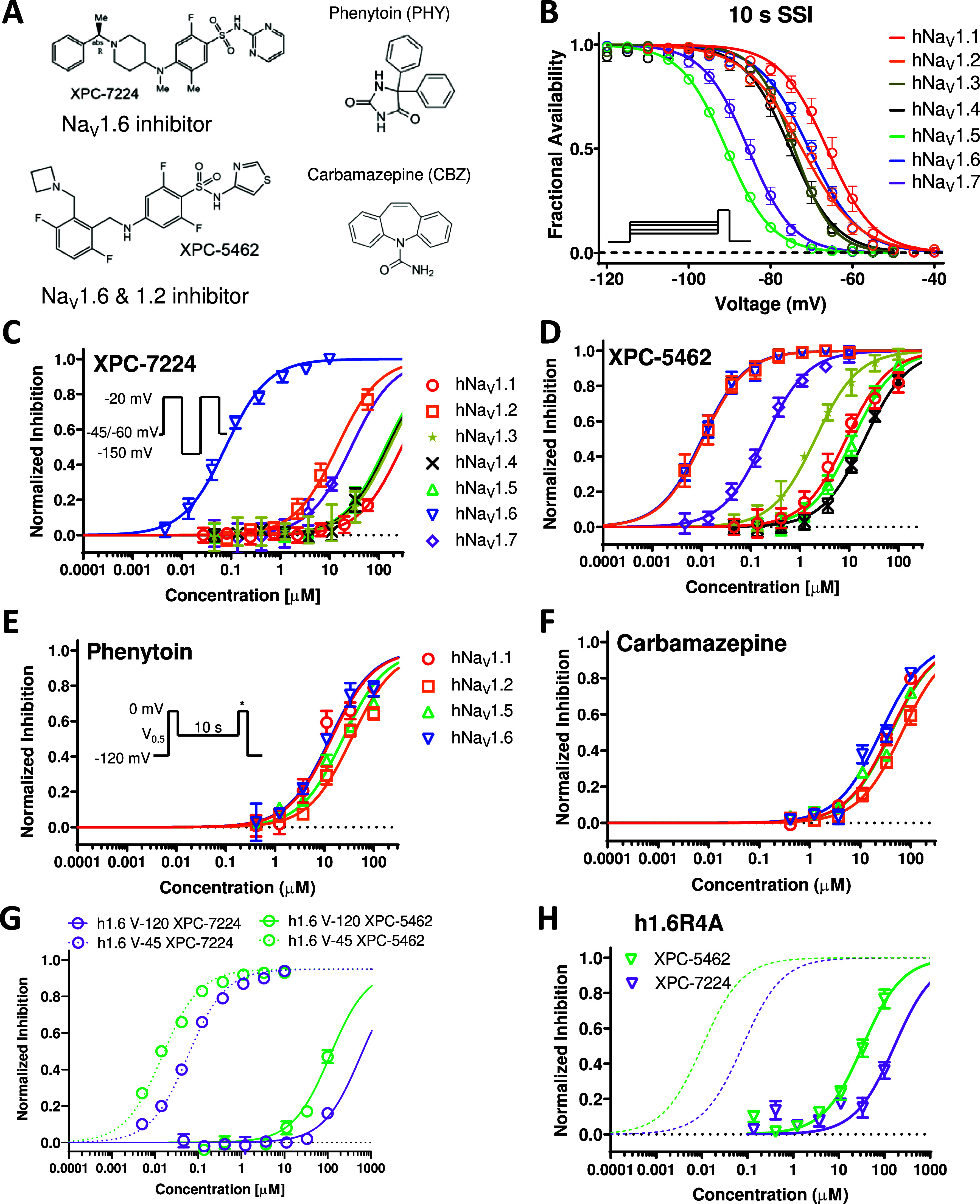
Comparative pharmacology of molecularly selective state dependent inhibitors compared with nonselective ASMs. (A) Structures of XPC compounds and classic pore-blocking ASMs, PHY and CBZ. (B) Normalized inactivation curves showing different voltage dependence of inactivation across human NaV subtypes hNaV1.1 (n = 11 cells), hNaV1.2 (n = 12 cells), hNaV1.5 (n = 63 cells), hNaV1.6 (n = 13 cells), and hNaV1.7 (n = 8 cells) (C) Potency of XPC-7224 plotted as fractional inhibition of different channel subtypes and fitted with a Hill equation, n = 3–11 cells per concentration. (D) Potency of XPC-5462, n = 3–11 cells per concentration. (E, F) Potency of the pore blocking ASMs measured using a protocol to capture compounds with fast off rates, n = 3–9 cells per concentration. (G) Membrane holding voltage dependence of potency for XPC-7224 (n = 3–5 cells per concentration) and XPC-5462 (n = 3–7 cells per data point). (H) Potencies for h1.6R4A channels for XPC-7224 (n = 3–6 cells per concentration) and XPC-5462 (n = 3–7 cells per concentration).
