Fig. 2. CBD attenuates nicotine intake at a moderate self-administered nicotine dose.
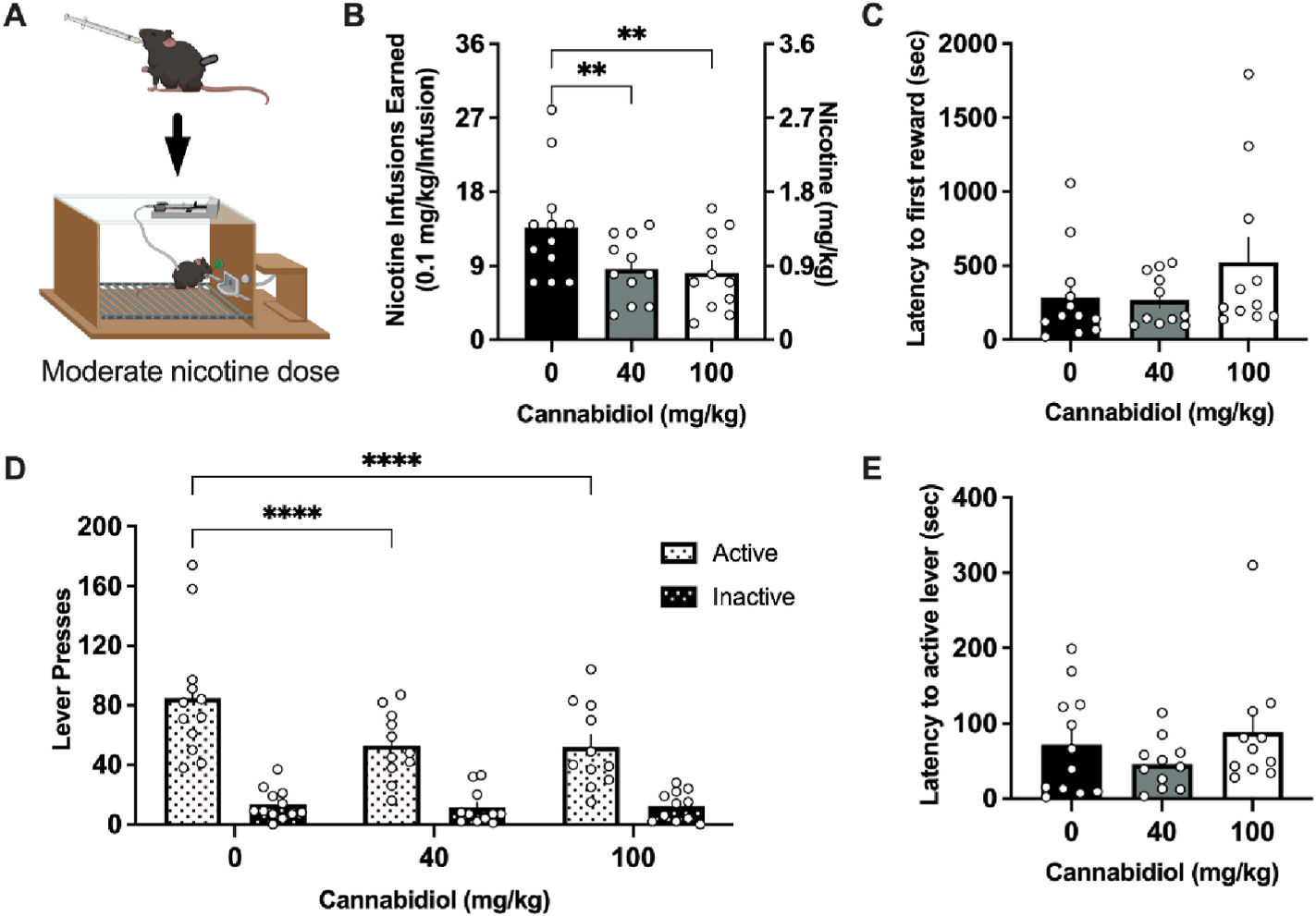
(A) Schematic of the experimental design with the moderate 0.1 mg/kg/infusion dose of nicotine, generated with Biorender.com (B) Male and female mice self-administering the moderate dose of nicotine significantly reduced the number of rewards earned following treatment with 40 and 100 mg/kg CBD. (C) Mice did not differ in the latency to the first nicotine infusion earned following CBD treatment. (D) Analysis of lever pressing behavior demonstrates a reduction in active lever responding at both the 40 and 100 mg/kg CBD doses. No statistical differences were observed in inactive lever pressing behavior across treatment. (E) Mice did not differ following CBD treatment in the latency to the first active lever press. Individual data points shown on graphs for each subject. Bar graphs represent mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.
