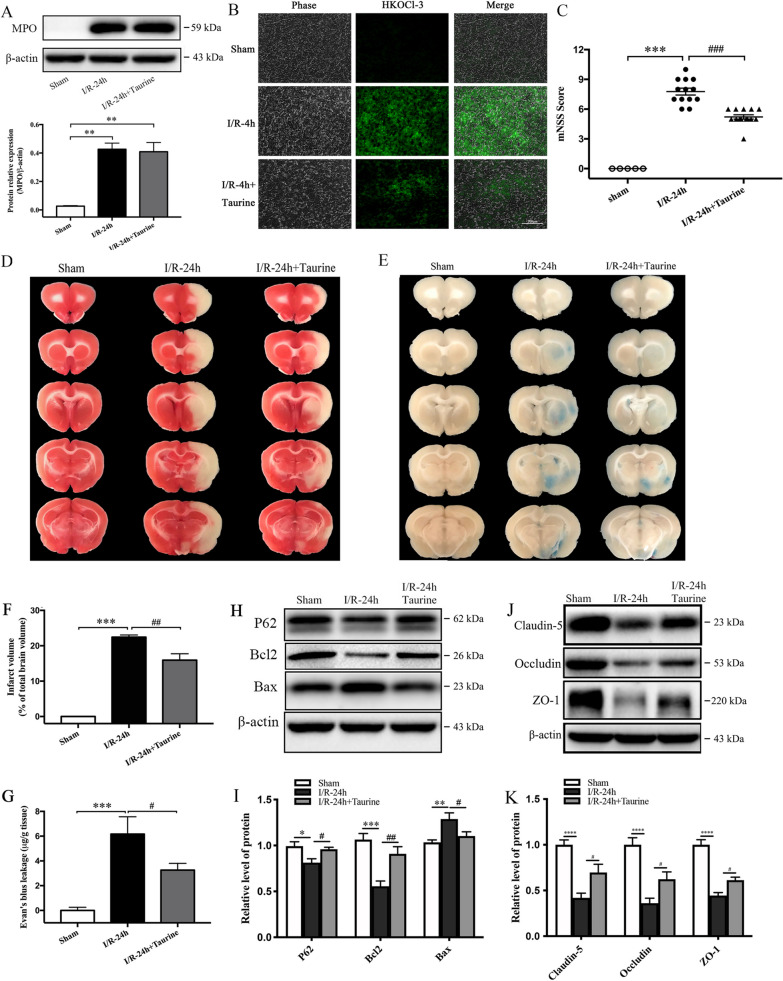
Fig. 7.
HOCl scavenger taurine reduced infarct volume, attenuated BBB disruption, and improved neurological function in rat brains after MCAO ischemia–reperfusion (I/R). I/R rats were subjected to 2 h of MCAO ischemia plus 24 h of reperfusion. Sham control rats were subjected to similar operation without MCAO. Taurine (Tau, 50 mg/kg) was intravenously administered at the onset of reperfusion. MPO expression and HOCl production were detected by western blot analysis and HKOCl-3 staining immunofluorescence, respectively. Infarct volumes were detected by TTC staining and quantitative analysis. A MPO expression in brain tissues. B HOCl production in the cortex of ischemic rat brains, bar = 200 μm. C Neurological deficit scores (mNSS). D, F Infarct volumes. E, G Evans blue leakage for the BBB permeability in I/R rat brains. H–I Western blot and quantitative analysis for P62, Bcl2 and Bax expression in I/R rat brains. J, K Western blot and quantitative analysis for tight junction proteins Claudin-5, Occludin and ZO-1 expression in I/R rat brains. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 compared to Sham group. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, compared to I-2 h/R-24 h group. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. (Statistical methods: A, I, K one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; C, F, G one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparisons test.)